A real-world comparison of tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T cells in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 36138152
- PMCID: PMC9556323
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01969-y
A real-world comparison of tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T cells in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Abstract
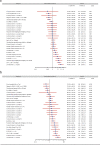
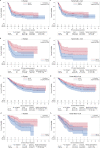
Axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) and tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel) have both demonstrated impressive clinical activity in relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). In this study, we analyzed the outcome of 809 patients with R/R DLBCL after two or more previous lines of treatment who had a commercial chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells order for axi-cel or tisa-cel and were registered in the retrospective French DESCAR-T registry study ( NCT04328298 ). After 1:1 propensity score matching (n = 418), the best overall response rate/complete response rate (ORR/CRR) was 80%/60% versus 66%/42% for patients treated with axi-cel compared to tisa-cel, respectively (P < 0.001 for both ORR and CRR comparisons). After a median follow-up of 11.7 months, the 1-year progression-free survival was 46.6% for axi-cel and 33.2% for tisa-cel (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.61; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.46-0.79; P = 0.0003). Overall survival (OS) was also significantly improved after axi-cel infusion compared to after tisa-cel infusion (1-year OS 63.5% versus 48.8%; HR = 0.63; 95% CI, 0.45-0.88; P = 0.0072). Similar findings were observed using the inverse probability of treatment weighting statistical approach. Grade 1-2 cytokine release syndrome was significantly more frequent with axi-cel than with tisa-cel, but no significant difference was observed for grade ≥3. Regarding immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS), both grade 1-2 and grade ≥3 ICANS were significantly more frequent with axi-cel than with tisa-cel. In conclusion, our matched comparison study supports a higher efficacy and also a higher toxicity of axi-cel compared to tisa-cel in the third or more treatment line for R/R DLBCL.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report the following competing interests: E.B.: consulting fees or honoraria from Novartis, Kite/Gilead, Roche, Takeda and Incyte; research funding (paid to institution) from Amgen; and travel and personal fees from Roche and Incyte. S.L.G.: honoraria from Janssen-Cilag, Kite/Gilead and Novartis. P.S.: honoraria or consultancy form Chugaï, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis and Kite/Gilead. T.G.: honoraria from Kite/Gilead, Pfizer and Takeda. S.G.: honoraria from Kite/Gilead, Incyte, Takeda and Janssen. P.B.: honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Kite/Gilead, Novartis and Abbvie. R.H.: honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Kite/Gilead, Incyte, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Takeda, Novartis and Roche. F.M.: consulting fees or honoraria from Genmab, Novartis, Kite/Gilead, Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Epizyme, Roche, Abbvie, Chugaï, Janssen, Incyte, Kymera, Miltenyi and Roche; and expert testimony for Roche. O.H.: consultancy for AB Science and Inatherys; and research funding (paid to institution) from Bristol Myers Squibb and Alexion. G.C.: consulting fees and honoraria from Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, Onwards Therapeutics, MedxCell, EmerCell, MabQ, Sanofi, Abbvie, Takeda, Roche, Janssen, Roche, Novartis and Myltenyi. M.L.: honoraria or travel grants from Pfizer, Novartis, Gilead and Bristol Myers Squibb. R.O.C.: consultancy and honoraria from Roche, Takeda, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Kite/Gilead, Abbvie and ADC Therapeutics; and research funding from Roche, Takeda and Kite/Gilead. J.A.: consulting fees and honoraria from Roche and Janssen-Cilag; S.C.: consulting fees and honoraria from Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Janssen, Takeda, Atara, Pierre Fabre, Kite/Gilead and Viatris. C.C.L.: honoraria from Kite/Gilead; D.B.: honoraria from Kite/Gilead. J.J.T.: consulting fees and honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb and Kite/Gilead. M.M.: consulting fees and honoraria from Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Takeda, Novartis and Sanofi; and research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen and Sanofi; F.X.G.: honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis and Kite/Gilead; L.D.L.R.: honoraria from Kite/Gilead; M.T.R.: honoraria from Novartis and Kite/Gilead. C.T.: consulting fees and honoraria from Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Bayer, Abbvie, Gilead Sciences, Roche, Janssen, Kite, Incyte and Amgen; and educational activities for Janssen, Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb and Novartis. R.D.B.: honoraria, consulting and personal fees from Janssen, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Kite/Gilead and Novartis.
Figures








Comment in
-
Clash of the titans: axi-cel versus tisa-cel for advanced-stage DLBCL.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023 Jan;20(1):5-6. doi: 10.1038/s41571-022-00711-4. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36380065 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (eds Swerdlow, S. et al) (IARC Publications, 2008).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

