Immunomodulatory effects of carbon ion radiotherapy in patients with localized prostate cancer
- PMID: 36138265
- PMCID: PMC10349746
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04194-9
Immunomodulatory effects of carbon ion radiotherapy in patients with localized prostate cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Radiotherapy is one of the main local treatment modalities for prostate cancer, while immunosuppressive effect induced by radiotherapy is an important factor of radiation resistance and treatment failure. Carbon ion radiotherapy (CIRT) is a novel radiotherapy technique and the immunomodulatory effect of CIRT provides the possibility of overcoming radioresistance and improving efficacy. The aim of this study was to assess the immune response evoked by CIRT in localized prostate cancer patients.
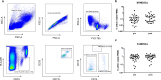
Methods: Thirty-two patients were treated by CIRT combined with or without hormone therapy and peripheral blood samples were collected before and after CIRT. Investigation of peripheral immune cell frequency, proliferation, and cytokine expression was conducted by flow cytometry, real-time quantitative PCR and ELISA.
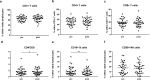
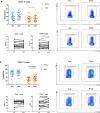
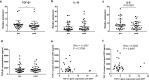
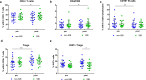
Results: There were no significant differences in the frequencies of CD3 + , CD4 + , CD8 + T cells and NK cells after CIRT. CD4/CD8 ratio increased whereas B cells decreased. All lymphocyte subsets except regulatory T cells (Tregs) displayed increased proliferation and T cells exhibited increased functionality after CIRT, characterized by modestly increased cytokine secretion of TNF. Moreover, higher frequencies of Tregs were shown. Neither monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) nor early MDSCs changed after CIRT. TGF-β1 gene expression decreased while IL-6 showed a non-significant trend towards a decrease. Both IL-10 gene expression and plasma TGF-β1 level were unchanged.
Conclusion: CIRT demonstrates the potential to elicit immune activation in localized prostate cancer patients, based on sparing lymphocytes, increased lymphocyte proliferation, enhanced T-cell functionality, together with limited induction of immunosuppressive cells and reduced expression of immunosuppressive cytokines.
Keywords: Carbon ion radiotherapy; Immune response; Immunomodulatory effect; Peripheral immune cells; Prostate cancer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Belka C, Ottinger H, Kreuzfelder E, Weinmann M, Lindemann M, Lepple-Wienhues A et al (1999) Impact of localized radiotherapy on blood immune cells counts and function in humans. Radiother Oncol 50:199–204 - PubMed
-
- Bronte V, Zanovello P (2005) Regulation of immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nat Rev Immunol 5:641–654 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

