Eliminating exogenous insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes by duodenal ablation and GLP-1RA decreases risk scores for cardiovascular events
- PMID: 36138441
- PMCID: PMC9503196
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-022-01628-z
Eliminating exogenous insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes by duodenal ablation and GLP-1RA decreases risk scores for cardiovascular events
Abstract
Introduction: Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) is an endoscopic ablation technique aimed at improving glycaemia and metabolic health in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). DMR has an insulin sensitizing effect in patients with T2DM. Reducing hyperinsulinemia can improve cardiovascular health. In the INSPIRE trial, we combined a single DMR with a glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) and demonstrated elimination of insulin treatment in 69% of patients at 6 months and 53% of patients at 18 months while improving glycaemic control and metabolic health. We hypothesized that this treatment approach is associated with improved cardiovascular health, by reducing hyperinsulinemia.
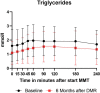
Methods: Before and 6 months after starting the combination treatment to replace insulin, the following assessments were performed to evaluate cardiovascular health: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to measure abdominal visceral adipose tissue volume, ambulatory 24 h blood pressure (ABPM) analysis, postprandial insulin and triglycerides, fasting lipid panel and urine microalbumin. The Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) score was calculated to estimate 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease or stroke and the diabetes lifetime-perspective prediction (DIAL) score was calculated to estimate years free of cardiovascular disease.
Results: Six months after replacing exogenous insulin by DMR and GLP-1RA, visceral adipose tissue decreased significantly by 24%. Postprandial triglyceride and insulin concentrations decreased significantly (p < 0.001), as did total cholesterol (from median 3.64 (IQR 3.34-4.89) to 3.48 (3.18-3.97) mmol/l, p = 0.008), LDL (from median 1.92 (IQR 1.49-2.30) to 1.79 (1.49-2.08 mmol/l, p = 0.044), and urine microalbumin (from median 7 (IQR 3-27) to 4 (3-8) mg/l, p = 0.018). All daytime blood pressure values decreased significantly. The ASCVD 10-year risk score decreased (from median 13.6 (IQR 5.7-26.0) to 11.5 (4.2-22.5) %, p = 0.030)) and the DIAL score increased (from median 82 (IQR 81-83) to 83 (81-84) years, (p = 0.039)).
Discussion: The combination of DMR and GLP-1RA to replace insulin therapy in patients with T2DM is associated with a positive effect on multiple parameters of cardiovascular health. Taken together, they show a pattern of overall improvement in cardiovascular health, as evidenced by decreased risk scores for cardiovascular complications. However, it is not yet clear whether these improvements will translate into a true reduction in cardiovascular events.
Keywords: DMR; Diabetes type 2; Duodenal ablation; Endoscopy; GLP-1 and duodenum.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MN is supported by a personal ZONMW-VICI grant 2020 [09150182010020]. JB received consultancy fees for participation in advisory board meeting for Fractyl Laboratories in 2019, and consultancy for Endogenex and Digma in 2021.
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes F. IDF Diabetes Atlas. Ninth edition ed. www.diabetesatlas.org2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

