Spectroscopic methods for COVID-19 detection and early diagnosis
- PMID: 36138463
- PMCID: PMC9502632
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-022-01867-2
Spectroscopic methods for COVID-19 detection and early diagnosis
Abstract
The coronavirus pandemic is a worldwide hazard that poses a threat to millions of individuals throughout the world. This pandemic is caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which was initially identified in Wuhan, China's Hubei provincial capital, and has since spread throughout the world. According to the World Health Organization's Weekly Epidemiological Update, there were more than 250 million documented cases of coronavirus infections globally, with five million fatalities. Early detection of coronavirus does not only reduce the spread of the virus, but it also increases the chance of curing the infection. Spectroscopic techniques have been widely used in the early detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 using Raman, Infrared, mass spectrometry and fluorescence spectroscopy. In this review, the reported spectroscopic methods for COVID-19 detection were discussed with emphasis on the practical aspects, limitations and applications.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Fluorescence spectroscopy; Infrared spectroscopy; Mass spectrometry; Raman spectroscopy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no competing interests.
Figures
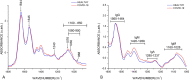
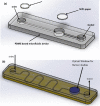
Similar articles
-
Geographical tracking and mapping of coronavirus disease COVID-19/severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) epidemic and associated events around the world: how 21st century GIS technologies are supporting the global fight against outbreaks and epidemics.Int J Health Geogr. 2020 Mar 11;19(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12942-020-00202-8. Int J Health Geogr. 2020. PMID: 32160889 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insights into COVID-19 Pathophysiology, Immune Pathogenesis, Detection, and Treatment.DNA Cell Biol. 2021 Jul;40(7):858-868. doi: 10.1089/dna.2021.0068. Epub 2021 May 14. DNA Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33989051 Review.
-
The spatial transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in China under the prevention and control measures at the early outbreak.Arch Public Health. 2021 Jan 13;79(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13690-021-00529-z. Arch Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33441168 Free PMC article.
-
Two years of COVID-19 pandemic: where are we now?J Microbiol. 2022 Mar;60(3):235-237. doi: 10.1007/s12275-022-1679-x. J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35235176 Free PMC article.
-
Novel coronavirus pandemic: A clinical overview.S Afr Fam Pract (2004). 2020 Jun 26;62(1):e1-e5. doi: 10.4102/safp.v62i1.5123. S Afr Fam Pract (2004). 2020. PMID: 32633997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical impact of rapid molecular diagnostic tests in patients presenting with viral respiratory symptoms: A systematic literature review.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 13;19(6):e0303560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303560. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38870136 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence-based multi-spectrum analysis for molecular fingerprint detection of SARS-CoV-2.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 23;104(21):e41928. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041928. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40419915 Free PMC article.
-
A feasibility study on exhaled breath analysis using UV spectroscopy to detect COVID-19.J Breath Res. 2023 Nov 2;18(1):016004. doi: 10.1088/1752-7163/ad0646. J Breath Res. 2023. PMID: 37875100 Free PMC article.
-
Smartphone-based point-of-care testing of the SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review.Sci Afr. 2023 Sep;21:e01757. doi: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2023.e01757. Epub 2023 Jun 10. Sci Afr. 2023. PMID: 37351482 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive meta-analysis and systematic review of breath analysis in detection of COVID-19 through Volatile organic compounds.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024 Jul;109(3):116309. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2024.116309. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38692202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manekiya M, Donelli M. Monitoring the covid-19 diffusion by combining wearable biosensors and smartphones. Prog Electromagn Res M. 2021;100:13–21. doi: 10.2528/PIERM20101905. - DOI
-
- Suresh Kumar S, Dashtipour K, Abbasi QH, Imran MA, Ahmad W. A review on wearable and contactless sensing for COVID-19 with policy challenges. Front Commun Netw. 2021;2:1–10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

