Anthropometric Indicators of the Cardiometabolic Risk, Muscle Strength, and Functional Capacity of Schoolchildren with Intellectual Disabilities during Lockdown in Chile
- PMID: 36138624
- PMCID: PMC9497658
- DOI: 10.3390/children9091315
Anthropometric Indicators of the Cardiometabolic Risk, Muscle Strength, and Functional Capacity of Schoolchildren with Intellectual Disabilities during Lockdown in Chile
Abstract
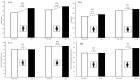
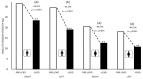
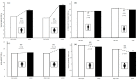
Lockdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic has negatively impacted the social, psychological, and physical well-being of the world population. In the case of people with intellectual disabilities, the impact of lockdown on their physical condition and functionality is not completely clear. This study aimed to determine the effects of COVID-19 lockdown on the anthropometric indicators of cardiometabolic risk, muscle strength, and functionality on schoolchildren with intellectual disabilities. The sample was composed of 132 students of both sexes (n = 74 pre-lockdown; n = 58 lockdown) belonging to two special education centers from the Metropolitan Region of Santiago, Chile. Our results showed significant reductions (p ≤ 0.05) in absolute and relative handgrip strength, as well as in functionality, when comparing pre-lockdown and lockdown measurements, with a greater loss in girls than boys. The design and implementation of physical exercise programs centered on strength training are necessary for the physical and functional reconditioning of this population. These programs need to be implemented in special education centers considering the general well-being, quality of life and work needs of people with intellectual disabilities.
Keywords: COVID-19; cardiometabolic risk; functional capacity; handgrip strength; intellectual disability; lockdown; muscle strength; physical condition; schoolchildren.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization What We Know about Long-Term Effects of COVID-19 (Coronavirus Update 36) 2020. [(accessed on 14 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/update-36-long-term-effects-of-c....
-
- Michalsen H., Wangberg S.C., Hartvigsen G., Jaccheri L., Muzny M., Henriksen A., Olsen M.I., Thrane G., Jahnsen R.B., Pettersen G., et al. Actividad física con soporte de mHealth a medida para personas con discapacidades intelectuales: Protocolo para un ensayo controlado aleatorizado. Protoc. De Investig. JMIR. 2020;9:e19213. doi: 10.2196/19213. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

