t6A and ms2t6A Modified Nucleosides in Serum and Urine as Strong Candidate Biomarkers of COVID-19 Infection and Severity
- PMID: 36139072
- PMCID: PMC9496545
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12091233
t6A and ms2t6A Modified Nucleosides in Serum and Urine as Strong Candidate Biomarkers of COVID-19 Infection and Severity
Abstract
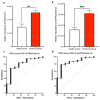
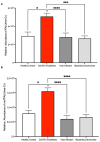
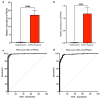
SARS-CoV-2 infection alters cellular RNA content. Cellular RNAs are chemically modified and eventually degraded, depositing modified nucleosides into extracellular fluids such as serum and urine. Here we searched for COVID-19-specific changes in modified nucleoside levels contained in serum and urine of 308 COVID-19 patients using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). We found that two modified nucleosides, N6-threonylcarbamoyladenosine (t6A) and 2-methylthio-N6-threonylcarbamoyladenosine (ms2t6A), were elevated in serum and urine of COVID-19 patients. Moreover, these levels were associated with symptom severity and decreased upon recovery from COVID-19. In addition, the elevation of similarly modified nucleosides was observed regardless of COVID-19 variants. These findings illuminate specific modified RNA nucleosides in the extracellular fluids as biomarkers for COVID-19 infection and severity.
Keywords: COVID-19; LC-MS; modified nucleosides.
Conflict of interest statement
K.T. was funded by Shimadzu Corporation and AiSTI Science Corporation. Other authors have no competing interest.
Figures
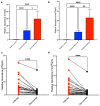
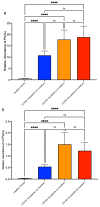
References
-
- Sugiyama M., Kinoshita N., Ide S., Nomoto H., Nakamoto T., Saito S., Ishikane M., Kutsuna S., Hayakawa K., Hashimoto M., et al. Serum CCL17 level becomes a predictive marker to distinguish between mild/moderate and severe/critical disease in patients with COVID-19. Gene. 2021;766:145145. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145145. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ruan Y., Hu B., Liu Z., Liu K., Jiang H., Li H., Li R., Luan Y., Liu X., Yu G., et al. No detection of SARS-CoV-2 from urine, expressed prostatic secretions, and semen in 74 recovered COVID-19 male patients: A perspective and urogenital evaluation. Andrology. 2021;9:99–106. doi: 10.1111/andr.12939. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

