A Panax quinquefolius-Based Preparation Prevents the Impact of 5-FU on Activity/Exploration Behaviors and Not on Cognitive Functions Mitigating Gut Microbiota and Inflammation in Mice
- PMID: 36139563
- PMCID: PMC9496716
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14184403
A Panax quinquefolius-Based Preparation Prevents the Impact of 5-FU on Activity/Exploration Behaviors and Not on Cognitive Functions Mitigating Gut Microbiota and Inflammation in Mice
Abstract
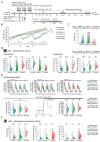
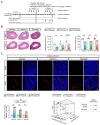
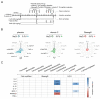
Chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (CRCI) and fatigue constitute common complaints among cancer patient survivors. Panax quinquefolius has been shown to be effective against fatigue in treated cancer patients. We developed a behavioral C57Bl/6j mouse model to study the role of a Panax quinquefolius-based solution containing vitamin C (Qiseng®) or vitamin C alone in activity/fatigue, emotional reactivity and cognitive functions impacted by 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) chemotherapy. 5-FU significantly reduces the locomotor/exploration activity potentially associated with fatigue, evokes spatial cognitive impairments and leads to a decreased neurogenesis within the hippocampus (Hp). Qiseng® fully prevents the impact of chemotherapy on activity/fatigue and on neurogenesis, specifically in the ventral Hp. We observed that the chemotherapy treatment induces intestinal damage and inflammation associated with increased levels of Lactobacilli in mouse gut microbiota and increased expression of plasma pro-inflammatory cytokines, notably IL-6 and MCP-1. We demonstrated that Qiseng® prevents the 5-FU-induced increase in Lactobacilli levels and further compensates the 5-FU-induced cytokine release. Concomitantly, in the brains of 5-FU-treated mice, Qiseng® partially attenuates the IL-6 receptor gp130 expression associated with a decreased proliferation of neural stem cells in the Hp. In conclusion, Qiseng® prevents the symptoms of fatigue, reduced chemotherapy-induced neuroinflammation and altered neurogenesis, while regulating the mouse gut microbiota composition, thus protecting against intestinal and systemic inflammation.
Keywords: IL-6; Panax quinquefolius-based solution; activity and exploration; behavioral mouse model; chemotherapy; cognitive functions; gut microbiota; intestinal inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Renaud Parment, Martine Dubois, Laurence Desrues, Alexandre Mutel, Kléouforo-Paul Dembélé, Nicolas Belin, Laure Tron, Pascal Hilber, Moïse Coëffier, Vincent Compère and David Ribet have no biomedical financial interests or no conflicts of interest to declare. Pr Florence Joly reports having received lecture and consulting fees from Janssen-Cilag, Astellas Pharma, Bayer, Sanofi and research funding from Astellas Pharma. Hélène Castel reports having received research funding from Laboratoire Natsuca. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results”. Céline Féger provided expert review of the written paper.
Figures





References
-
- Joly F., Heutte N., Duclos B., Noal S., Léger-Hardy I., Dauchy S., Longato N., Desrues L., Houede N., Lange M., et al. Prospective Evaluation of the Impact of Antiangiogenic Treatment on Cognitive Functions in Metastatic Renal Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus. 2016;2:642–649. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2016.04.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lange M., Joly F., Vardy J., Ahles T., Dubois M., Tron L., Winocur G., De Ruiter M.B., Castel H. Cancer-related cognitive impairment: An update on state of the art, detection, and management strategies in cancer survivors. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019;30:1925–1940. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz410. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Silverman D.H.S., Dy C.J., Castellon S.A., Lai J., Pio B.S., Abraham L., Waddell K., Petersen L., Phelps M.E., Ganz P.A. Altered frontocortical, cerebellar, and basal ganglia activity in adjuvant-treated breast cancer survivors 5–10 years after chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007;103:303–311. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9380-z. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

