Quality-of-Life Evaluation of Patients with Unresectable Locally Advanced or Locally Recurrent Head and Neck Carcinoma Treated with Head and Neck Photoimmunotherapy
- PMID: 36139573
- PMCID: PMC9496661
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14184413
Quality-of-Life Evaluation of Patients with Unresectable Locally Advanced or Locally Recurrent Head and Neck Carcinoma Treated with Head and Neck Photoimmunotherapy
Abstract
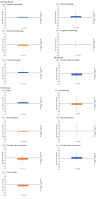
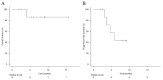
Head and neck photoimmunotherapy (HN-PIT), a new treatment developed for local control of head and neck carcinoma, uses cetuximab sarotalocan sodium with a laser system to specifically destroy only tumor cells. No studies have examined the impact of HN-PIT on the quality of life (QOL) of patients with head and neck cancer. This study assessed the QOL of patients with unresectable locally advanced or locally recurrent head and neck carcinoma (LA/LR-HNC) treated with HN-PIT. Nine eligible patients with unresectable LA/LR-HNC who underwent HN-PIT at our institution between 20 January 2021 and 30 April 2022 were included in the study. They completed a QOL evaluation form. The primary endpoint was QOL assessment. The secondary endpoints were overall response rate, overall survival (OS), progression-free survival, and adverse events. QOL was compared before and 4 weeks after HN-PIT. There were no significant changes in all QOL assessment parameters after treatment with HN-PIT. The overall response rate was 89%, and safety was acceptable. For patients with unresectable LA/LR-HNC, HN-PIT provided good local control without decreasing the QOL. The addition of HN-PIT to conventional head and neck carcinoma treatment may lead to the prolongation of OS in head and neck carcinoma.
Keywords: cetuximab sarotalocan sodium; head and neck photoimmunotherapy; quality of life; unresectable locally advanced or locally recurrent head and neck carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines): Head and Neck Cancers Version 2.2022. 2022. [(accessed on 4 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/head-and-neck.pdf.
-
- Burtness B., Harrington K.J., Greil R., Soulières D., Tahara M., de Castro G., Psyrri A., Basté N., Neupane P., Bratland Å., et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (keynote-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2019;394:1915–1928. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32591-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

