Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Tool in Nanomedicine and Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 36139610
- PMCID: PMC9497055
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14184450
Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Tool in Nanomedicine and Cancer Treatment
Abstract
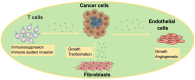
Extracellular vesicles are membrane-bound vesicles released by cells to mediate intercellular communication and homeostasis. Various external stimuli as well as inherent abnormalities result in alterations in the extracellular vesicle milieu. Changes to cells result in alterations in the content of the extracellular vesicle biogenesis, which may affect proximal and distal cells encountering these altered extracellular vesicles. Therefore, the examination of changes in the extracellular vesicle signature can be used to follow disease progression, reveal possible targets to improve therapy, as well as to serve as mediators of therapy. Furthermore, recent studies have developed methods to alter the cargo of extracellular vesicles to restore normal function or deliver therapeutic agents. This review will examine how extracellular vesicles from cancer cells differ from normal cells, how these altered extracellular vesicles can contribute to cancer progression, and how extracellular vesicles can be used as a therapeutic agent to target cancer cells and cancer-associated stroma. Here we present extracellular vesicles as a novel tool in nanomedicine.
Keywords: cancer; cancer treatments; cancer vaccine; drug delivery; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; gene delivery; mesenchymal stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles; nanoparticles; protein delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

