Nanocarrier System: State-of-the-Art in Oral Delivery of Astaxanthin
- PMID: 36139750
- PMCID: PMC9495775
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11091676
Nanocarrier System: State-of-the-Art in Oral Delivery of Astaxanthin
Abstract
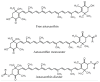
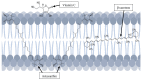
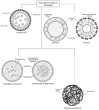
Astaxanthin (3,3'-dihydroxy-4,4'-diketo-β-β carotene), which belongs to the xanthophyll class, has shown potential biological activity in in vitro and in vivo models including as a potent antioxidant, anti-lipid peroxidation and cardiovascular disease prevention agent. It is mainly extracted from an alga, Haematococcus pluvialis. As a highly lipid-soluble carotenoid, astaxanthin has been shown to have poor oral bioavailability, which limits its clinical applications. Recently, there have been several suggestions and the development of various types of nano-formulation, loaded with astaxanthin to enhance their bioavailability. The employment of nanoemulsions, liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles, chitosan-based and PLGA-based nanoparticles as delivery vehicles of astaxanthin for nutritional supplementation purposes has proven a higher oral bioavailability of astaxanthin. In this review, we highlight the pharmacological properties, pharmacokinetics profiles and current developments of the nano-formulations of astaxanthin for its oral delivery that are believed to be beneficial for future applications. The limitations and future recommendations are also discussed in this review.
Keywords: antioxidants; astaxanthin; bioavailability; carotenoids; nanoparticles; oral delivery; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yamashita E. Astaxanthin as a Medical Food. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2013;3:254–258. doi: 10.31989/ffhd.v3i7.49. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials