Zinc Application Mitigates Copper Toxicity by Regulating Cu Uptake, Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes, and Improving Physiological Characteristics in Summer Squash
- PMID: 36139763
- PMCID: PMC9495343
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11091688
Zinc Application Mitigates Copper Toxicity by Regulating Cu Uptake, Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes, and Improving Physiological Characteristics in Summer Squash
Abstract
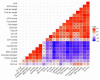
Zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu) are essential micronutrients for the plant's growth, development, and metabolism, but in high concentrations, the elements disrupt normal metabolic processes. The present study investigated the effects of different concentrations (added to a Hogland-based solution) of zinc (control, 5, 10 mg L-1 ZnSO4) and copper (control, 0.1, 0.2 mg L-1 CuSO4) on the growth characteristics and biochemical indices of summer squash (Cucurbita pepo L.). Compared with control, a single application of Cu or Zn at both concentrations significantly declined fruit yield, growth traits, pigments content, and high content of these minerals and values of stress-related indices. Increased Cu concentration in the nutritional solutions reduced the activity of ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and guaiacol peroxidase (GPX). Copper at high concentrations intensified ROS production, aggravated oxidative stresses, and decreased the plant yield and productivity. Nonetheless, combining Cu and Zn could alleviate stress intensity by boosting antioxidant enzymes, redox regulation, and a resultant diminishment in the content of H2O2, proline, malondialdehyde, and minerals. The obtained results corroborate that the co-application of zinc in Cu-contaminated areas can improve the plant's economic yield and physiological parameters by hindering copper toxicity and enhancing the photosynthetic capacity.
Keywords: antioxidant enzymes; copper toxicity; summer squash; zinc application.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmadi H., Babalar M., Sarcheshmeh M.A.A., Morshedloo M.R., Shokrpour M. Effects of exogenous application of citrulline on prolonged water stress damages in hyssop (Hyssopus officinalis L.): Antioxidant activity, biochemical indices, and essential oils profile. Food Chem. 2020;333:127433. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127433. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi H., Morshedloo M.R., Emrahi R., Javanmard A., Rasouli F., Maggi F., Kumar M., Lorenzo J.M. Introducing three new fruit-scented mints to farmlands: Insights on drug yield, essential-oil quality, and antioxidant properties. Antioxidants. 2022;11:866. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050866. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morshedloo M.R., Fereydouni S., Ahmadi H., Hassanpouraghdam M.B., Aghaee A., Mehrabani L.V., Maggi F. Natural diversity in fatty acids profiles and antioxidant properties of sumac fruits (Rhus coriaria L.): Selection of preferable populations for food industries. Food Chem. 2022;374:131757. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131757. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

