Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin as a Prognostic Factor for Severe COVID-19 ARDS
- PMID: 36139946
- PMCID: PMC9495198
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11091166
Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin as a Prognostic Factor for Severe COVID-19 ARDS
Abstract
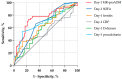
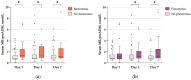
Mid-regional proadrenomedullin (MR-proADM) protects against endothelial permeability and has been associated with prognosis in bacterial sepsis. As endothelial dysfunction is central in the pathophysiology of severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, we sought to evaluate MR-proADM both as a prognostic biomarker and as a marker of bacterial superinfection. Consecutive patients admitted to the ICU for severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia were prospectively included and serum was bio-banked on days 1, 3, and 7. MR-proADM levels were measured blindly from clinical outcomes in batches at the end of follow-up. Among the 135 patients included between April 2020 and May 2021, 46 (34.1%) had died at day 60. MR-proADM levels on days 1, 3, and 7 were significantly higher in day-60 non-survivors. The area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (0.744, p < 0.001) of day-1 MR-proADM compared favorably with the AUC ROC curve of day-1 procalcitonin (0.691, p < 0.001). Serial MR-proADM measurements on days 3 and 7 may add prognostic information. After adjusting for CRP, LDH, and lymphocyte values, day-1 MR-proADM remained significantly associated with day-60 mortality. MR-proADM concentrations were significantly higher in patients with respiratory superinfections (on days 3 and 7) and bloodstream infections (on days 1, 3, and 7) than in patients without infection. Our results suggest that MR-proADM is a good predictor of outcome in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection and could be a useful tool to assess bacterial superinfection in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; Mid-regional Pro-adrenomedullin; SARS-CoV-2; biomarker; prognosis; superinfection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors received a research grant from Thermo Fisher to perform the study. Outside of the study, J.-F.T. declares a participation to the boards of Merck, Pfizer, BD, Gilead and Paratek, and lecture fees for Pfizer, Shionogi, BD and Merck.
Figures


References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 22 August 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int.
-
- Bonaventura A., Vecchié A., Dagna L., Martinod K., Dixon D.L., Van Tassell B.W., Dentali F., Montecucco F., Massberg S., Levi M., et al. Endothelial Dysfunction and Immunothrombosis as Key Pathogenic Mechanisms in COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021;21:319–329. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00536-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

