Carbon Nanotube and Its Derived Nanomaterials Based High Performance Biosensing Platform
- PMID: 36140116
- PMCID: PMC9496036
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12090731
Carbon Nanotube and Its Derived Nanomaterials Based High Performance Biosensing Platform
Abstract
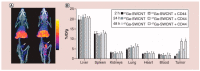
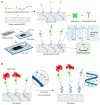
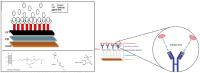
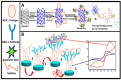
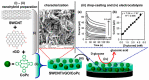
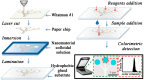
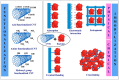
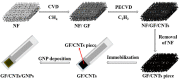
After the COVID-19 pandemic, the development of an accurate diagnosis and monitoring of diseases became a more important issue. In order to fabricate high-performance and sensitive biosensors, many researchers and scientists have used many kinds of nanomaterials such as metal nanoparticles (NPs), metal oxide NPs, quantum dots (QDs), and carbon nanomaterials including graphene and carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Among them, CNTs have been considered important biosensing channel candidates due to their excellent physical properties such as high electrical conductivity, strong mechanical properties, plasmonic properties, and so on. Thus, in this review, CNT-based biosensing systems are introduced and various sensing approaches such as electrochemical, optical, and electrical methods are reported. Moreover, such biosensing platforms showed excellent sensitivity and high selectivity against not only viruses but also virus DNA structures. So, based on the amazing potential of CNTs-based biosensing systems, healthcare and public health can be significantly improved.
Keywords: carbon nanotubes; high-performance biosensors; nanomaterials-based biosensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


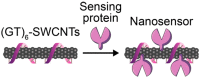
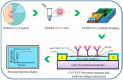

References
-
- Justino C.I.L., Rocha-Santos T.A., Duarte A.C., Rocha-Santos T.A. Review of Analytical Figures of Merit of Sensors and Biosensors in Clinical Applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010;29:1172–1183. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2010.07.008. - DOI
-
- Guo S., Dong S. Biomolecule-Nanoparticle Hybrids for Electrochemical Biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009;28:96–109. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2008.10.014. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

