Identification of Key Genes and Pathways in Genotoxic Stress Induced Endothelial Dysfunction: Results of Whole Transcriptome Sequencing
- PMID: 36140167
- PMCID: PMC9495888
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10092067
Identification of Key Genes and Pathways in Genotoxic Stress Induced Endothelial Dysfunction: Results of Whole Transcriptome Sequencing
Abstract
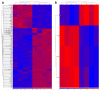
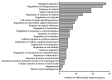
Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality worldwide. Endothelial disfunction underlying the atherogenesis can be triggered by genotoxic stress in endothelial cells. In the presented research whole transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) of human coronary artery (HCAEC) and internal thoracic artery (HITAEC) endothelial cells in vitro exposed to 500 ng/mL mitomycin C (treatment group) or 0.9% NaCl (control group) was performed. Resulting to bioinformatic analysis, 56 upregulated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and 6 downregulated DEGs with absolute fold change ≥ 2 and FDR p-value < 0.05 were selected in HCAEC exposed to mitomycin C compared to the control group; in HITAEC only one upregulated DEG was found. According to Gene Ontology enrichment analysis, DEGs in HCAEC were classified into 25 functional groups of biological processes, while in HITAEC we found no statistically significant (FDR p-value < 0.05) groups. The four largest groups containing more than 50% DEGs (“signal transduction”, “response to stimulus”, “biological regulation”, and “regulation of biological process”) were identified. Finally, candidate DEGs and pathways underlying the genotoxic stress induced endothelial disfunction have been discovered that could improve our understanding of fundamental basis of atherogenesis and help to justification of genotoxic stress as a novel risk factor for atherosclerosis.
Keywords: DNA damage; RNA-seq; atherogenesis; bioinformatic analysis; differentially expressed genes; endothelial disfunction; gene ontology enrichment; genotoxic stress; mutagenesis; transcriptomic signature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteomic Profiling of Endothelial Cells Exposed to Mitomycin C: Key Proteins and Pathways Underlying Genotoxic Stress-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 5;25(7):4044. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074044. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612854 Free PMC article.
-
[Genotoxic stress leads to the proinflammatory response of endothelial cells: an in vitro study].Biomed Khim. 2022 Nov;68(5):361-366. doi: 10.18097/PBMC20226805361. Biomed Khim. 2022. PMID: 36373882 Russian.
-
Mitomycin C induced genotoxic stress in endothelial cells is associated with differential expression of proinflammatory cytokines.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2020 Oct-Dec;858-860:503252. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2020.503252. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2020. PMID: 33198933
-
[Transcription of DNA-Methyltransferases in Endothelial Cells Exposed to Mitomycin C].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2022 May-Jun;56(3):491-497. doi: 10.31857/S0026898422030156. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2022. PMID: 35621104 Russian.
-
[The gene expression signature in endothelial cells exposed to mitomycin C].Biomed Khim. 2021 Mar;67(2):130-136. doi: 10.18097/PBMC20216702130. Biomed Khim. 2021. PMID: 33860769 Russian.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Profiling of Endothelial Cells Exposed to Mitomycin C: Key Proteins and Pathways Underlying Genotoxic Stress-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 5;25(7):4044. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074044. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612854 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Omics Profiling of Human Endothelial Cells from the Coronary Artery and Internal Thoracic Artery Reveals Molecular but Not Functional Heterogeneity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 9;24(19):15032. doi: 10.3390/ijms241915032. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834480 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin Can Modulate DNA Damage Repair in Endothelial Cells Exposed to Mitomycin C.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 5;24(7):6783. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076783. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047754 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of endothelial cell dysfunction in atherosclerosis: a new perspective integrating traditional and modern approaches.Front Physiol. 2025 Mar 26;16:1555118. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1555118. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40206381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

