Rational Generation of Monoclonal Antibodies Selective for Pathogenic Forms of Alpha-Synuclein
- PMID: 36140270
- PMCID: PMC9496384
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10092168
Rational Generation of Monoclonal Antibodies Selective for Pathogenic Forms of Alpha-Synuclein
Abstract
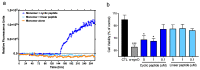
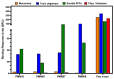
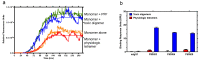
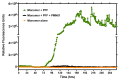
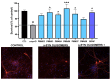
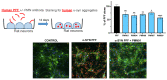
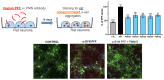
Misfolded toxic forms of alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of synucleinopathies, including Parkinson's disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA). The α-Syn oligomers and soluble fibrils have been shown to mediate neurotoxicity and cell-to-cell propagation of pathology. To generate antibodies capable of selectively targeting pathogenic forms of α-Syn, computational modeling was used to predict conformational epitopes likely to become exposed on oligomers and small soluble fibrils, but not on monomers or fully formed insoluble fibrils. Cyclic peptide scaffolds reproducing these conformational epitopes exhibited neurotoxicity and seeding activity, indicating their biological relevance. Immunization with the conformational epitopes gave rise to monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) with the desired binding profile showing selectivity for toxic α-Syn oligomers and soluble fibrils, with little or no reactivity with monomers, physiologic tetramers, or Lewy bodies. Recognition of naturally occurring soluble α-Syn aggregates in brain extracts from DLB and MSA patients was confirmed by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). In addition, the mAbs inhibited the seeding activity of sonicated pre-formed fibrils (PFFs) in a thioflavin-T fluorescence-based aggregation assay. In neuronal cultures, the mAbs protected primary rat neurons from toxic α-Syn oligomers, reduced the uptake of PFFs, and inhibited the induction of pathogenic phosphorylated aggregates of endogenous α-Syn. Protective antibodies selective for pathogenic species of α-Syn, as opposed to pan α-Syn reactivity, are expected to provide enhanced safety and therapeutic potency by preserving normal α-Syn function and minimizing the diversion of active antibody from the target by the more abundant non-toxic forms of α-Syn in the circulation and central nervous system.
Keywords: aggregation-based technologies and therapeutics; alpha-synuclein; conformational epitope; fibril; misfolding specific antibody; oligomer; protein aggregation; selectivity; sequence/structure determinants; synucleinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
N.R.C., J.M.K. and B.Z. are current employees of ProMIS Neurosciences. E.G., S.S.P., S.C.C.H., A.A. and X.P. have received consultation compensation from ProMIS Neurosciences. E.G., S.S.P. and B.Z. possess ProMIS stock options. N.R.C. and J.M.K. possess ProMIS shares and stock options. S.S.P. is the inventor on patent applications for Collective Coordinates computational modeling. S.S.P., N.R.C., X.P. and J.M.K. are inventors on patent applications relating to conformation-specific epitopes in alpha-synuclein, antibodies thereto and methods related thereof. The work presented was financially supported by ProMIS Neurosciences. A.R., J.W., C.S., C.K.Y. and S.-E.N. declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

