Primary Bone Tumors of the Spine-Proposal for Treatment Based on a Single Centre Experience
- PMID: 36140664
- PMCID: PMC9498005
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12092264
Primary Bone Tumors of the Spine-Proposal for Treatment Based on a Single Centre Experience
Abstract
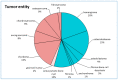
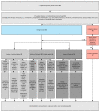
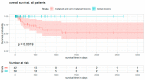
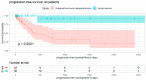
This study reports a large single-center series of primary bone tumors of the spine (PBTs). We aimed to review the concepts for management, as this kind of tumor represents a very rare entity, and also propose a new treatment algorithm. Retrospective analysis revealed 92 patients receiving surgery for PBTs from 2007 to 2019 at our center. They were analyzed based on surgical management and the course of the disease. A total of 145 surgical procedures were performed (50 cervical, 46 thoracic, 28 lumbar, and 21 sacral). Complete tumor resection was achieved in 65%, of which 22% showed tumor recurrence during follow-up (mean time to recurrence 334 days). The five-year mortality rate was significantly lower after complete resection (3% versus 25% after subtotal resection). Most of the patients improved in their symptoms through surgery. Regarding the tumor entity, the most common PBTs were vertebral hemangiomas (20%), osteoid osteomas (15%), and chordomas (16%). The Enneking graduation system showed a good correlation with the risk of recurrence and mortality. Complete resection in PBTs increased survival rates and remains the method of choice. Thus, quality of life-especially with a higher extent of resection-should be considered.
Keywords: outcomes; primary bone tumor; treatment strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pinter N.K., Pfiffner T.J., Mechtler L.L. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Volume 136. Elsevier B.V.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2016. Neuroimaging of spine tumors; pp. 689–706. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

