Hawthorn Juice Simulation System for Pectin and Polyphenol Adsorption Behavior: Kinetic Modeling Properties and Identification of the Interaction Mechanism
- PMID: 36140941
- PMCID: PMC9498233
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11182813
Hawthorn Juice Simulation System for Pectin and Polyphenol Adsorption Behavior: Kinetic Modeling Properties and Identification of the Interaction Mechanism
Abstract
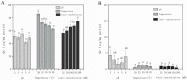
The interaction between polyphenols and polysaccharides plays an important role in increasing the turbidity stability of fruit juice and improving unpleasant sensory experiences. The binding adsorption behavior between hawthorn pectin (HP) and polyphenols (epicatechin and chlorogenic acid) accorded with the monolayer adsorption behavior driven by chemical action and were better fitted by pseudo-second order dynamic equation and Langmuir model. The HP binding sites (Qm) and adsorption capacity (Qe) to epicatechin were estimated at 75.188 and 293.627 μg/mg HP, respectively, which was about nine and twelve times higher than that of chlorogenic acid. The interaction between HP and polyphenols exhibited higher turbidity characteristics, particle size and lower zeta potential than epicatechin and chlorogenic acid alone. Meanwhile, according to Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) analysis, it could be speculated that the interaction between HP and polyphenols resulted in chemical combination. Moreover, ΔH < 0 and TΔS < 0, which indicated that the interaction between HP and polyphenols was mainly driven by hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces.
Keywords: chlorogenic acid; epicatechin; hawthorn; non-covalent interaction; pectin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Adsorption isotherm studies on the interaction between polyphenols and apple cell walls: Effects of variety, heating and drying.Food Chem. 2019 Jun 1;282:58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.12.098. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30711106
-
Investigation of the interaction mechanism of citrus pectin-polyphenol-protein complex.Food Chem. 2025 Mar 15;468:142419. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.142419. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39700817
-
The Physicochemical Properties and Antioxidant Activities of the Hawthorn Pectin Extracted Using Ultra-High Pressure Assisted Acid Extraction (UPAAE).Foods. 2024 Mar 23;13(7):983. doi: 10.3390/foods13070983. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38611292 Free PMC article.
-
Food Applications and Potential Health Benefits of Hawthorn.Foods. 2022 Sep 15;11(18):2861. doi: 10.3390/foods11182861. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36140986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in interactions between polyphenols and plant cell wall polysaccharides as studied using an adsorption technique.Food Chem. 2022 Mar 30;373(Pt B):131487. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131487. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 34741970 Review.
References
-
- Rababa’h A.M., Al Yacoub O.N., El-Elimat T., Rabab’ah M., Altarabsheh S., Deo S., Al-Azayzih A., Zayed A., Alazzam S., Alzoubi K.H. The effect of hawthorn flower and leaf extract (Crataegus spp.) on cardiac hemostasis and oxidative parameters in Sprague Dawley rats. Heliyon. 2020;6:e04617. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04617. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ma L., Xu G.B., Tang X.Y., Zhang C., Zhao W., Wang J., Chen H. Anti-cancer potential of polysaccharide extracted from hawthorn (Crataegus.) on human colon cancer cell line HCT116 via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. J. Funct. Foods. 2020;64:103677. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103677. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

