Study on Active Particles in Air Plasma and Their Effect on α-Amylase
- PMID: 36141025
- PMCID: PMC9498710
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11182896
Study on Active Particles in Air Plasma and Their Effect on α-Amylase
Abstract
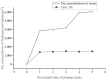
As a new technology for food processing, plasma has good prospects for protein modification. This study investigated the effect of plasma on the activity of the α-amylase. The composition of the active particles in air plasma generated by spark discharge was analyzed and determined. Furthermore, the quantitative analysis of the active particles such as H2O2, O3, and -OH was made by the chemical detection method. Powdered α-amylase was treated with plasma in various conditions, in which α-amylase and the variation of α-amylase activity under the action of air plasma were quantitatively analyzed. The results showed that the concentration of active particles in the system was positively correlated with the action time for air plasma. After 5 min of plasma action, the concentration of O3 and H2O2 was large enough for food disinfection, but the concentration of -OH was smaller and its lifetime was extremely short. Moreover, it was determined that the optimum action time for the activation of solid powdered α-amylase by air plasma was 120 s. With higher energy, the air plasma acts directly on solid powdered α-amylase to destroy its spatial structure, resulting in enzyme inactivation, sterilization, and disinfection.
Keywords: active particle composition; enzymolysis activity; plasma; α-amylase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
[Study on Chemical Kinetic Effect of Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma].Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2015 Mar;35(3):706-10. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2015. PMID: 26117883 Chinese.
-
Mechanisms of Active Substances in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Reactor: Species Determination, Interaction Analysis, and Contribution to Chlorobenzene Removal.Environ Sci Technol. 2021 Mar 16;55(6):3956-3966. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c04914. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Environ Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 33629580
-
Effects of Pulsed Electric Field (PEF) Treatment on Enhancing Activity and Conformation of α-Amylase.Protein J. 2016 Apr;35(2):154-62. doi: 10.1007/s10930-016-9649-y. Protein J. 2016. PMID: 26897374
-
Encouragement of Enzyme Reaction Utilizing Heat Generation from Ferromagnetic Particles Subjected to an AC Magnetic Field.PLoS One. 2015 May 19;10(5):e0127673. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127673. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25993268 Free PMC article.
-
A brief overview on the application and sources of α-amylase and expression hosts properties in order to production of recombinant α-amylase.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2022 Apr;69(2):650-659. doi: 10.1002/bab.2140. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2022. PMID: 33655550 Review.
References
-
- Liu T., Zeng Y., Xue X., Sui Y., Liang Y., Wang F., Feng F., Kim J. He-Plasma Jet Generation and Its Application for E. coli Sterilization. J. Spectrosc. 2021;2021:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2021/6671531. - DOI
-
- Misra N.N., Tiwari B.K., Raghavarao K.S.M.S., Cullen P.J. Nonthermal Plasma Inactivation of Food-Borne Pathogens. Food Eng. Rev. 2011;3:159–170. doi: 10.1007/s12393-011-9041-9. - DOI
-
- Mackinder M.A., Wang K., Zheng B., Shrestha M., Fan Q.H. Magnetic field enhanced cold plasma sterilization. Plasma Med. 2020;17–18:100092. doi: 10.1016/j.cpme.2019.100092. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

