Effects of Regular Brazil Nut (Bertholletia excelsa H.B.K.) Consumption on Health: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials
- PMID: 36141050
- PMCID: PMC9498495
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11182925
Effects of Regular Brazil Nut (Bertholletia excelsa H.B.K.) Consumption on Health: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials
Abstract
The Brazil nut (BN) is a promising food due to its numerous health benefits, but it is still necessary to systematically review the scientific evidence on these benefits. Thus, we examined the effects of regular BN consumption on health markers in humans according to the health state (with specific diseases or not) of the subjects. PubMed, Embase®, and Scielo databases were used to search for clinical trials. The PRISMA guideline was used to report the review, and the risk of bias for all studies was assessed. Twenty-four studies were included in the present review, of which fifteen were non-randomized. BNs were consumed in the context of a habitual free-living diet in all studies. Improvement in antioxidant status through increased levels of selenium and/or glutathione peroxidase activity in plasma, serum, whole blood, and/or erythrocytes was observed in all studies that evaluated antioxidant status, regardless of the health state of the sample. In addition, healthy subjects improved lipid markers and fasting glucose. Subjects with obesity had improvement in markers of lipid metabolism. Subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus or dyslipidemia improved oxidative stress or DNA damage. Subjects undergoing hemodialysis benefited greatly from BN consumption, as they improved lipid profile markers, oxidative stress, inflammation, and thyroid function. Older adults with mild cognitive impairment improved verbal fluency and constructional praxis, and controversial results regarding the change in a marker of lipid peroxidation were observed in subjects with coronary artery disease. In conclusion, the benefits of BN consumption were found in different pathways of action and study populations.
Keywords: functional foods; metabolic risk factors; nutrition; nuts; oilseeds; selenium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

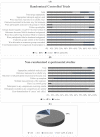

References
-
- INC Global Statistical Review, Brazil Nuts. [(accessed on 3 September 2022)]. Available online: https://www.nutfruit.org/industry/news/detail/global-statistical-review-....
-
- Cheng A., Raai M.N., Zain N.A.M., Massawe F., Singh A., Wan-Mohtar W.A.A.Q.I. In Search of Alternative Proteins: Unlocking the Potential of Underutilized Tropical Legumes. Food Secur. 2019;11:1205–1215. doi: 10.1007/s12571-019-00977-0. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

