Decoding 'Maximum Entropy' Deconvolution
- PMID: 36141124
- PMCID: PMC9497885
- DOI: 10.3390/e24091238
Decoding 'Maximum Entropy' Deconvolution
Abstract
For over five decades, the mathematical procedure termed "maximum entropy" (M-E) has been used to deconvolve structure in spectra, optical and otherwise, although quantitative measures of performance remain unknown. Here, we examine this procedure analytically for the lowest two orders for a Lorentzian feature, obtaining expressions for the amount of sharpening and identifying how spurious structures appear. Illustrative examples are provided. These results enhance the utility of this widely used deconvolution approach to spectral analysis.
Keywords: deconvolution; maximum entropy; spectral analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

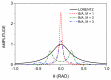
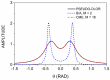

References
-
- Burg J.P. Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis. Stanford University; Stanford, CA, USA: 1975. Stanford Exploration Project.
-
- Ulrych T. Maximum Entropy Power Spectrum of Long Period Geomagnetic Reversals. Nature. 1972;235:218–219. doi: 10.1038/235218a0. - DOI
-
- Willingale R. Use of the maximum entropy method in X-ray astronomy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1981;194:359–364. doi: 10.1093/mnras/194.2.359. - DOI
-
- Narayan R., Nityananda R. Maximum Entropy Image Restoration in Astronomy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1986;24:127–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.aa.24.090186.001015. - DOI
-
- Wells J.W., Birkinshaw K. A matrix approach to resolution enhancement of XPS spectra by a modified maximum entropy method. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2006;152:37–43. doi: 10.1016/j.elspec.2006.03.003. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

