The Role of Thymoquinone in Inflammatory Response in Chronic Diseases
- PMID: 36142148
- PMCID: PMC9499585
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810246
The Role of Thymoquinone in Inflammatory Response in Chronic Diseases
Abstract
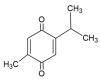
Anti-inflammatory therapies have been shown to be effective in the prevention of various cardiovascular diseases, tumors, and cancer complications. Thymoquinone (TQ), the main active constituent of Nigella sativa, has shown promising therapeutic properties in many in vivo and in vitro models. However, TQ has poor bioavailability and is hydrophobic, prohibiting clinical trials with TQ alone. Studies have explored the combination of TQ with biological nanomaterials to improve its bioavailability. The TQ nanoparticle formulation shows better bioavailability than free TQ, and these formulations are ready for clinical trials to determine their potential as therapeutic agents. In this paper, we review current knowledge about the interaction between TQ and the inflammatory response and summarize the research prospects in Korea and abroad. We discuss the different biological activities of TQ and various combination therapies of TQ and nanomaterials in clinical trials.
Keywords: chronic disease; immunotherapeutic; inflammation; signaling pathways; thymoquinone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hannan M.A., Zahan M.S., Sarker P.P., Moni A., Ha H., Uddin M.J. Protective effects of black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its bioactive constituent, thymoquinone against kidney injury: An aspect on pharmacological insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:9078. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169078. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

