Effects of Global and Specific DNA-Binding Proteins on Transcriptional Regulation of the E. coli bgl Operon
- PMID: 36142257
- PMCID: PMC9499468
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810343
Effects of Global and Specific DNA-Binding Proteins on Transcriptional Regulation of the E. coli bgl Operon
Abstract
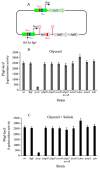
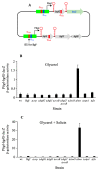
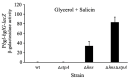
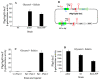
Using reporter gene (lacZ) transcriptional fusions, we examined the transcriptional dependencies of the bgl promoter (Pbgl) and the entire operon regulatory region (Pbgl-bglG) on eight transcription factors as well as the inducer, salicin, and an IS5 insertion upstream of Pbgl. Crp-cAMP is the primary activator of both Pbgl and the bgl operon, while H-NS is a strong dominant operon repressor but only a weak repressor of Pbgl. H-NS may exert its repressive effect by looping the DNA at two binding sites. StpA is a relatively weak repressor in the absence of H-NS, while Fis also has a weak repressive effect. Salicin has no effect on Pbgl activity but causes a 30-fold induction of bgl operon expression. Induction depends on the activity of the BglF transporter/kinase. IS5 insertion has only a moderate effect on Pbgl but causes a much greater activation of the bgl operon expression by preventing the full repressive effects of H-NS and StpA. While several other transcription factors (BglJ, RcsB, and LeuO) have been reported to influence bgl operon transcription when overexpressed, they had little or no effect when present at wild type levels. These results indicate the important transcriptional regulatory mechanisms operative on the bgl operon in E. coli.
Keywords: Crp; DNA loop; Fis; H-NS; StpA; bgl operon; insertion sequences (IS); β-glucosides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Independent regulation of H-NS-mediated silencing of the bgl operon at two levels: upstream by BglJ and LeuO and downstream by DnaKJ.Microbiology (Reading). 2005 Oct;151(Pt 10):3349-3359. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28080-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2005. PMID: 16207917
-
BglJ-RcsB heterodimers relieve repression of the Escherichia coli bgl operon by H-NS.J Bacteriol. 2010 Dec;192(24):6456-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.00807-10. Epub 2010 Oct 15. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20952573 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the yjjQ-bglJ operon, encoding LuxR-type transcription factors, and the divergent yjjP gene by H-NS and LeuO.J Bacteriol. 2008 Feb;190(3):926-35. doi: 10.1128/JB.01447-07. Epub 2007 Nov 30. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18055596 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of gene expression: cryptic β-glucoside (bgl) operon of Escherichia coli as a paradigm.Braz J Microbiol. 2015 Mar 4;45(4):1139-44. doi: 10.1590/s1517-83822014000400003. eCollection 2014. Braz J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25763016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The LeuO regulator and quiescence: About transcriptional roadblocks, multiple promoters, and crispr-cas.Mol Microbiol. 2022 Nov;118(5):503-509. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14990. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Mol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36203248 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone-like nucleoid structuring (H-NS) protein silences the beta-glucoside (bgl) utilization operon in Escherichia coli by forming a DNA loop.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Nov 12;20:6287-6301. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.11.027. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36420159 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Characterization of fucAO Operon Activation in Escherichia coli.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 2;25(7):3946. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073946. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612757 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of DNA-binding proteins on insertion sequence element transposition upstream of the bgl operon in Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 11;15:1388522. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1388522. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38666260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schnetz K., Toloczyki C., Rak B. Beta-glucoside (bgl) operon of Escherichia coli K-12: Nucleotide sequence, genetic organization, and possible evolutionary relationship to regulatory components of two Bacillus subtilis genes. J. Bacteriol. 1987;169:2579–2590. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2579-2590.1987. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

