The Rheology and Physicochemical Characteristics of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Their Clinical Implications
- PMID: 36142430
- PMCID: PMC9503994
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810518
The Rheology and Physicochemical Characteristics of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Their Clinical Implications
Abstract
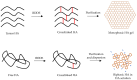
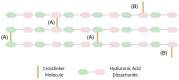
Hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers have become the most popular material for facial volume augmentation and wrinkle correction. Several filler brands are currently on the market all around the world and their features are extremely variable; for this reason, most users are unaware of their differences. The study of filler rheology has become a wellspring of knowledge, differentiating HA fillers, although these properties are not described thoroughly by the manufacturers. The authors of this review describe the more useful rheological properties that can help clinicians understand filler characteristics and the likely correlation of these features with clinical outcomes.
Keywords: hyaluronic acid fillers; physicochemical properties; rheology.
Conflict of interest statement
S.P.F., G.S. and D.M.H.M have consultancy contracts with RELIFE S.r.l. S.I. is the Head of Scientific Affairs at RELIFE S.r.l.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rheologic and Physicochemical Characteristics of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Overview and Relationship to Product Performance.Facial Plast Surg. 2022 Apr;38(2):116-123. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1741560. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Facial Plast Surg. 2022. PMID: 35114708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rheology of hyaluronic acid and dynamic facial rejuvenation: Topographical specificities.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018 Oct;17(5):736-743. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12774. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 30311427
-
Advanced Concepts in Rheology for the Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Soft Tissue Fillers.Dermatol Surg. 2021 May 1;47(5):e159-e167. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000002916. Dermatol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33492870 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of a monophasic hyaluronic acid filler in the correction of nasolabial folds: A randomized, multicenter, single blinded, split-face study.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018 Aug;17(4):584-589. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12380. Epub 2017 Sep 14. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 28913927 Clinical Trial.
-
Hyaluronic Acid Fillers in Soft Tissue Regeneration.Facial Plast Surg. 2017 Feb;33(1):87-96. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1597685. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Facial Plast Surg. 2017. PMID: 28226376 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Evaluation of Injectability Attributes in OxiFree™ Dermal Fillers: MaiLi® Product Variants and Clinical Case Reports.Gels. 2024 Apr 19;10(4):276. doi: 10.3390/gels10040276. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667695 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative in-vitro degradation of hyaluronic acids exposed to different hyaluronidase enzymes.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2025 Jan-Feb;15(1):178-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2025.01.001. Epub 2025 Jan 13. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2025. PMID: 39897433 Free PMC article.
-
Lip Volumization With Hyaluronic Acid: Comparative Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cannula and Needle Techniques in a Multicenter Study.Cureus. 2025 Feb 19;17(2):e79325. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79325. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40125164 Free PMC article.
-
Etiology of Delayed Inflammatory Reaction Induced by Hyaluronic Acid Filler.Arch Plast Surg. 2024 Feb 7;51(1):20-26. doi: 10.1055/a-2184-6554. eCollection 2024 Jan. Arch Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38425859 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Functionalization of Hyaluronan Dermal Fillers with Vitamin B3: Efficient Combination of Bio-Stimulation Properties with Hydrogel System Resilience Enhancement.Gels. 2024 May 24;10(6):361. doi: 10.3390/gels10060361. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38920908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons Plastic Surgery Statistics Report 2020. [(accessed on 15 May 2022)]. Available online: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2020/cosmetic-p....
-
- Saljoughian M. Benefits and Risk of Facial Fillers. US Pharm. 2019;44:9–12.
-
- Signorini M., Liew S., Sundaram H., De Boulle K.L., Goodman G.J., Monheit G., Wu Y., Trindade de Almeida A.R., Swift A., Vieira Braz A., et al. Global Aesthetics Consensus: Avoidance and Management of Complications from Hyaluronic Acid Fillers—Evidence- and Opinion-Based Review and Consensus Recommendations. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016;137:961e–971e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000002184. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

