Genome-Wide Identification of Laminin Family Related to Follicular Pseudoplacenta Development in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii)
- PMID: 36142434
- PMCID: PMC9504374
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810523
Genome-Wide Identification of Laminin Family Related to Follicular Pseudoplacenta Development in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii)
Abstract
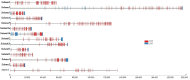
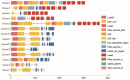
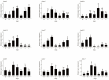
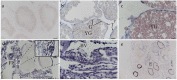
As major elements of the basement membrane, laminins play a significant role in angiogenesis, migration, and adhesion of various cells. Sebastes schlegelii is a marine viviparous teleost of commercial importance. Previous research has reported abundant blood vessels and connective tissue in the ovary during gestation. In this study, 14 laminin genes of the α, β, and γ subfamilies from genomic data were identified based on zebrafish and human laminins, distributed on 9 chromosomes in S. schlegelii. Analysis of structural domains showed that coiled-coil regions and EGF domains existed in all laminin genes. Moreover, via qPCR, we found that the expression of laminin genes, including lama4, lama5, lamb4, lamc1, and lamc3, gradually increased from the phase III ovary stage and peaked in the early stage of gestation, especially lama4 and lama5 which showed dramatically increased expression at the blastula stage. Accordingly, in situ hybridization of lama4 was conducted. The results revealed that signals became stronger following the phase IV ovary stage, and the strongest signals were located on the follicular pseudoplacenta at the blastula stage. These results suggest that the high expression of laminin genes, especially lama4 after fertilization, may drive cell proliferation, migration, and tissue expansion in the S. schlegelii ovary and ultimately promote follicular pseudoplacenta formation.
Keywords: Sebastes schlegelii; evolution; follicular pseudoplacenta; laminin genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
New insights on folliculogenesis and follicular placentation in marine viviparous fish black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii).Gene. 2022 Jun 15;827:146444. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146444. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35378250
-
Sequencing of the black rockfish chromosomal genome provides insight into sperm storage in the female ovary.DNA Res. 2019 Dec 1;26(6):453-464. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsz023. DNA Res. 2019. PMID: 31711192 Free PMC article.
-
Structures, evolutionary relationships and expression profiles of the tumour necrosis factor superfamily and their receptors in black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii).Dev Comp Immunol. 2022 Jul;132:104405. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2022.104405. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Dev Comp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35364135
-
Molecular characterization and expression analysis of foxo3l in response to exogenous hormones in black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii).Gene. 2020 Aug 30;753:144777. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144777. Epub 2020 May 16. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32428695
-
The Bdkrb2 gene family provides a novel view of viviparity adaptation in Sebastes schlegelii.BMC Ecol Evol. 2021 Mar 17;21(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12862-021-01774-0. BMC Ecol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33731008 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
FOXP2 overexpression upregulates LAMA4 expression and thereby alleviates preeclampsia by regulating trophoblast behavior.Commun Biol. 2024 Nov 1;7(1):1427. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07149-7. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39487340 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and Epigenomic Responses to Cortisol-Mediated Stress in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Skeletal Muscle.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 10;25(14):7586. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147586. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062828 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

