α-Bisabolol Attenuates Doxorubicin Induced Renal Toxicity by Modulating NF-κB/MAPK Signaling and Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in Rats
- PMID: 36142441
- PMCID: PMC9502245
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810528
α-Bisabolol Attenuates Doxorubicin Induced Renal Toxicity by Modulating NF-κB/MAPK Signaling and Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in Rats
Abstract
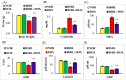
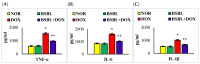
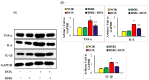
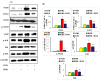
Doxorubicin (DOX) is a well-known and effective antineoplastic agent of the anthracycline family. But, multiple organ toxicities compromise its invaluable therapeutic usage. Among many toxicity types, nephrotoxicity is one of the major concerns. In recent years many approaches, including bioactive agents of natural origin, have been explored to provide protective effects against chemotherapy-related complications. α-Bisabolol is a naturally occurring monocyclic sesquiterpene alcohol identified in the essential oils of various aromatic plants and possesses a wide range of pharmacological properties such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, cardioprotective, antibiotic, anti-irritant, and anticancer activities. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of α-Bisabolol on DOX-induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar male albino rats. Nephrotoxicity was induced in rats by injecting a single dose of DOX (12.5 mg/kg, i.p.), and the test compound, α-Bisabolol (25 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally along with DOX as a co-treatment daily for 5 days. DOX-injected rats showed reduction in body weight along with a concomitant fall in antioxidants and increased lipid peroxidation in the kidney. DOX-injection also increased levels/expressions of proinflammatory cytokines namely tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and inflammatory mediators like inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and activated nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB)/mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling in the kidney tissues. DOX also triggered apoptotic cell death, evidenced by the increased expression of pro-apoptotic markers like BCL2-Associated X Protein (Bax), cleaved caspase-3, caspase- 9, and cytochrome-C) and a decrease in the expressions of anti-apoptotic markers namely B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl2) and B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL) in the kidney. These biochemical alterations were additionally supported by light microscopic findings, which revealed structural alterations in the kidney. However, treatment with α-Bisabolol prevented body weight loss, restored antioxidants, mitigated lipid peroxidation, and inhibited the rise in proinflammatory cytokines, as well as favorably modulated the expressions of NF-κB/MAPK signaling and apoptosis markers in DOX-induced nephrotoxicity. Based on the results observed, it can be concluded that α-Bisabolol has potential to attenuate DOX-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation mediated activation of NF-κB/MAPK signaling alongwith intrinsic pathway of apoptosis in rats. The study findings are suggestive of protective potential of α-Bisabolol in DOX associated nephrotoxicity and this could be potentially useful in minimizing the adverse effects of DOX and may be a potential agent or adjuvant for renal protection.
Keywords: NF-κB/MAPK signaling; apoptosis; doxorubicin; nephrotoxicity; phytochemicals; renal toxicity; α-Bisabolol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
α-Bisabolol Attenuates NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Activation and ER-Stress-Mediated Apoptosis by Invoking Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Defense Systems against Doxorubicin-Induced Testicular Toxicity in Rats.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 3;14(21):4648. doi: 10.3390/nu14214648. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364909 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effect of herbacetin against cyclophosphamide-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022 Jan-Dec;41:9603271221132140. doi: 10.1177/09603271221132140. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36198566
-
Aegeline improves doxorubicin-induced liver toxicity by modulating oxidative stress and Bax/Bcl2/caspase/NF-κB signaling.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 26;15(1):27203. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09675-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40715307 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and biological effects of alpha-bisabolol: An updated review of the molecular mechanisms.Life Sci. 2022 Sep 1;304:120728. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120728. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35753438 Review.
-
The Effects of Polyphenols on Doxorubicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Modulating Inflammatory Cytokines, Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress, and Oxidative DNA Damage.Phytother Res. 2025 May;39(5):2147-2164. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8470. Epub 2025 Mar 16. Phytother Res. 2025. PMID: 40091446 Review.
Cited by
-
α-Bisabolol: A Dietary Sesquiterpene that Attenuates Apoptotic and Nonapoptotic Cell Death Pathways by Regulating the Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Hippo Signaling Axis in Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity in Rats.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Aug 6;7(9):2694-2705. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00108. eCollection 2024 Sep 13. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39296269 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage caused by chemotherapy has duality, and traditional Chinese medicine may be a better choice to reduce its toxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 22;15:1483160. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1483160. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39502534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hesperidin Nanoformulation: A Potential Strategy for Reducing Doxorubicin-Induced Renal Damage via the Sirt-1/HIF1-α/VEGF/NF-κB Signaling Cascade.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;17(9):1144. doi: 10.3390/ph17091144. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338308 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dulaglutide in Doxorubicin Induced Renal Toxicity in Rats.Biologics. 2025 Jul 3;19:399-412. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S523547. eCollection 2025. Biologics. 2025. PMID: 40630078 Free PMC article.
-
Myricetin protects against doxorubicin-induced acute kidney injury in rats by mitigating oxidative damage and apoptotic response.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 30;16:1601628. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1601628. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40661077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanajou D., Nazari Soltan Ahmad S., Hosseini V., Kalantary-Charvadeh A., Marandi Y., Roshangar L., Bahrambeigi S., Mesgari-Abbasi M. β-Lapachone protects against doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity via NAD(+)/AMPK/NF-kB in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2019;392:633–640. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01619-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ghibu S., Delemasure S., Richard C., Guilland J.C., Martin L., Gambert S., Rochette L., Vergely C. General oxidative stress during doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats: Absence of cardioprotection and low antioxidant efficiency of alpha-lipoic acid. Biochimie. 2012;94:932–939. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.02.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Afsar T., Razak S., Almajwal A., Al-Disi D. Doxorubicin-induced alterations in kidney functioning, oxidative stress, DNA damage, and renal tissue morphology; Improvement by Acacia hydaspica tannin-rich ethyl acetate fraction. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020;27:2251–2260. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.07.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

