Glial Cell-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 36142483
- PMCID: PMC9502483
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810572
Glial Cell-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
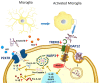
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder; it is the most common cause of dementia and has no treatment. It is characterized by two pathological hallmarks, the extracellular deposits of amyloid beta (Aβ) and the intraneuronal deposits of Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). Yet, those two hallmarks do not explain the full pathology seen with AD, suggesting the involvement of other mechanisms. Neuroinflammation could offer another explanation for the progression of the disease. This review provides an overview of recent advances on the role of the immune cells' microglia and astrocytes in neuroinflammation. In AD, microglia and astrocytes become reactive by several mechanisms leading to the release of proinflammatory cytokines that cause further neuronal damage. We then provide updates on neuroinflammation diagnostic markers and investigational therapeutics currently in clinical trials to target neuroinflammation.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; astrocytes; clinical trials; diagnostic markers; microglia; neuroinflammation; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The neuroprotective N-terminal amyloid-β core hexapeptide reverses reactive gliosis and gliotoxicity in Alzheimer's disease pathology models.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 May 27;20(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02807-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37245024 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Microglia and Astrocytes in Alzheimer's Disease: From Neuroinflammation to Ca2+ Homeostasis Dysregulation.Cells. 2022 Sep 1;11(17):2728. doi: 10.3390/cells11172728. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of microglia-associated neuroinflammation on Alzheimer's disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 22;14:1117172. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1117172. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating Neuroinflammation as a Prospective Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer's Disease.Cells. 2025 Jan 22;14(3):168. doi: 10.3390/cells14030168. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39936960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging Neuroinflammation: Quantification of Astrocytosis in a Multitracer PET Approach.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2785:195-218. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3774-6_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38427196
Cited by
-
Extra-Virgin Olive Oil in Alzheimer's Disease: A Comprehensive Review of Cellular, Animal, and Clinical Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 5;25(3):1914. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031914. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct Cell Reprogramming and Phenotypic Conversion: An Analysis of Experimental Attempts to Transform Astrocytes into Neurons in Adult Animals.Cells. 2023 Feb 14;12(4):618. doi: 10.3390/cells12040618. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advancement in bioeffect, metabolism, stability, and delivery systems of apigenin, a natural flavonoid compound: challenges and perspectives.Front Nutr. 2023 Jul 26;10:1221227. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1221227. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37565039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of New Pyrazolines As Small Molecule Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 13;9(29):31401-31409. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c10490. eCollection 2024 Jul 23. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39072133 Free PMC article.
-
A review on traditional Chinese medicine natural products and acupuncture intervention for Alzheimer's disease based on the neuroinflammatory.Chin Med. 2024 Feb 28;19(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00900-6. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38419106 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

