The Interplay between Aquaporin-1 and the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lung Injury Model in Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 36142499
- PMCID: PMC9502402
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810588
The Interplay between Aquaporin-1 and the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lung Injury Model in Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Abstract
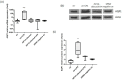
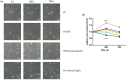
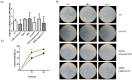
Aquaporin-1 (AQP1), a water channel, and the hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1A) are implicated in acute lung injury responses, modulating among others pulmonary vascular leakage. We hypothesized that the AQP1 and HIF1A systems interact, affecting mRNA, protein levels and function of AQP1 in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMECs) exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Moreover, the role of AQP1 in apoptosis and wound healing progression was examined. Both AQP1 mRNA and protein expression levels were higher in HPMECs exposed to LPS compared to untreated HPMECs. However, in the LPS-exposed HIF1A-silenced cells, the mRNA and protein expression levels of AQP1 remained unaltered. In the permeability experiments, a statistically significant volume increase was observed at the 360 s time-point in the LPS-exposed HPMECs, while LPS-exposed HIF1A-silenced HPMECs did not exhibit cell swelling, implying a dysfunctional AQP1. AQP1 did not seem to affect cell apoptosis yet could interfere with endothelial migration and/or proliferation. Based on our results, it seems that HIF1A silencing negatively affects AQP1 mRNA and protein expression, as well as AQP1 function, in the setting of lung injury.
Keywords: AQP1; HIF1A; HPMEC; LPS; lung injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AQP1 expression alterations affect morphology and water transport in Schwann cells and hypoxia-induced up-regulation of AQP1 occurs in a HIF-1α-dependent manner.Neuroscience. 2013 Nov 12;252:68-79. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.006. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23948641
-
Increased Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Aquaporin 1-Null Mice Is Mediated via Decreased Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 2α Stability.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Jun;54(6):882-91. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0363OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26649797
-
Functional and transcriptional induction of aquaporin-1 gene by hypoxia; analysis of promoter and role of Hif-1α.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028385. Epub 2011 Dec 7. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22174795 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 binding site in the induction of aquaporin-1 mRNA expression by hypoxia.DNA Cell Biol. 2011 Aug;30(8):539-44. doi: 10.1089/dna.2009.1014. Epub 2011 May 25. DNA Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21612401
-
Aqp-1 Gene Knockout Attenuates Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension of Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019 Jan;39(1):48-62. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311714. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30580569
Cited by
-
Expression and Regulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Signalling in Acute Lung Inflammation.Cells. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):29. doi: 10.3390/cells14010029. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39791730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD73: Friend or Foe in Lung Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 14;24(6):5545. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065545. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporin Expression and Regulation in Clinical and Experimental Sepsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 29;25(1):487. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010487. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Aquaporins in Human Studies: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential in Critical Illness.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 20;14(12):1688. doi: 10.3390/life14121688. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporin-1 Facilitates Macrophage M1 Polarization by Enhancing Glycolysis Through the Activation of HIF1α in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):1775-1790. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02154-8. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39365391
References
-
- Bernard G.R., Artigas A., Brigham K.L., Carlet J., Falke K., Hudson L., Lamy M., Legall J.R., Morris A., Spragg R. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994;149:818–824. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.3.7509706. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Singer M., Deutschman C.S., Seymour C.W., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M., Bellomo R., Bernard G.R., Chiche J.D., Coopersmith C.M., et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

