Modulating Activity Evaluation of Gut Microbiota with Versatile Toluquinol
- PMID: 36142608
- PMCID: PMC9505934
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810700
Modulating Activity Evaluation of Gut Microbiota with Versatile Toluquinol
Abstract
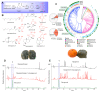
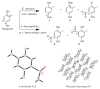
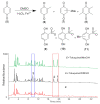
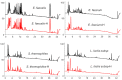
Gut microbiota have important implications for health by affecting the metabolism of diet and drugs. However, the specific microbial mediators and their mechanisms in modulating specific key intermediate metabolites from fungal origins still remain largely unclear. Toluquinol, as a key versatile precursor metabolite, is commonly distributed in many fungi, including Penicillium species and their strains for food production. The common 17 gut microbes were cultivated and fed with and without toluquinol. Metabolic analysis revealed that four strains, including the predominant Enterococcus species, could metabolize toluquinol and produce different metabolites. Chemical investigation on large-scale cultures led to isolation of four targeted metabolites and their structures were characterized with NMR, MS, and X-ray diffraction analysis, as four toluquinol derivatives (1-4) through O1/O4-acetyl and C5/C6-methylsulfonyl substitutions, respectively. The four metabolites were first synthesized in living organisms. Further experiments suggested that the rare methylsulfonyl groups in 3-4 were donated from solvent DMSO through Fenton's reaction. Metabolite 1 displayed the strongest inhibitory effect on cancer cells A549, A2780, and G401 with IC50 values at 0.224, 0.204, and 0.597 μM, respectively, while metabolite 3 displayed no effect. Our results suggest that the dominant Enterococcus species could modulate potential precursors of fungal origin and change their biological activity.
Keywords: Enterococcus faecalis; Enterococcus faecium; acetylation; antitumor; biotransformation; gut microbiota; toluquinol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Toluquinol, a marine fungus metabolite, is a new angiosuppresor that interferes with the Akt pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Jun 15;85(12):1727-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.04.007. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23603293
-
Synthesis and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Compounds Based on Toluquinol.Mar Drugs. 2019 Aug 23;17(9):492. doi: 10.3390/md17090492. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31450731 Free PMC article.
-
Novel application assigned to toluquinol: inhibition of lymphangiogenesis by interfering with VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 signalling pathway.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;173(12):1966-87. doi: 10.1111/bph.13488. Epub 2016 May 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27018653 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota Metabolism and Interaction with Food Components.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 23;21(10):3688. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103688. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32456257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biotransformation of dietary phytoestrogens by gut microbes: A review on bidirectional interaction between phytoestrogen metabolism and gut microbiota.Biotechnol Adv. 2020 Nov 1;43:107576. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107576. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Biotechnol Adv. 2020. PMID: 32531317 Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing in vivo synthesis of bioactive multiarylmethanes in Escherichia coli via oxygen-mediated free radical reaction induced by simple phenols.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Aug 6;23(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02494-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 39103877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krishnan Y.S., Ding N., Saedi M., Choi G.V., Sridharan D.H., Sherr M.L., Yarmush R.C., Alaniz A.J., Lee K. Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites modulate inflammatory response in hepatocytes and macrophages. Cell Rep. 2018;23:1099–1111. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hehemann J.H., Kelly A.G., Pudlo N.A., Martens E.C., Boraston A.B. Bacteria of the human gut microbiome catabolize red seaweed glycans with carbohydrate-active enzyme updates from extrinsic microbes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2012;109:19786–19791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211002109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

