Study on Enhancing the Corrosion Resistance and Photo-Thermal Antibacterial Properties of the Micro-Arc Oxidation Coating Fabricated on Medical Magnesium Alloy
- PMID: 36142610
- PMCID: PMC9503942
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810708
Study on Enhancing the Corrosion Resistance and Photo-Thermal Antibacterial Properties of the Micro-Arc Oxidation Coating Fabricated on Medical Magnesium Alloy
Abstract
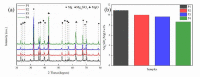
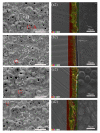
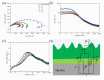
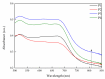
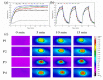
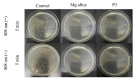
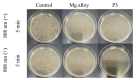
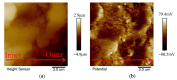
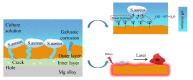
Photo-thermal antibacterial properties have attracted much attention in the biomedical field because of their higher antibacterial efficiency. Through fabricating micro-arc oxidation coatings with different treating current densities set on a Mg-Zn-Ca alloy, the present study tried to systematically investigate and optimize the corrosion resistance and photo-thermal antibacterial properties of MAO coatings. The results indicated that different current densities had great influence on the corrosion resistance and photo-thermal property of the MAO coatings, and a current density at 30 A·dm-2 exhibited the best corrosion resistance, light absorption capacity at 808 nm, and photo-thermal capability, simultaneously with good antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Escherichia coli (E. coli). This photo-thermal property of MAO coatings was probably related to the effect of current density on MgO content in the coating that could promote the separation of photo-generated electron carriers and hinder the recombination of photo-generated electron carriers and holes.
Keywords: anti-bacteria; corrosion resistance; magnesium alloy; micro-arc oxidation; photo-thermal therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Kopp A., Smeets R., Jung O., Kröger N., Klink A. Defined surface adjustment for medical magnesium implants by electrical discharge machining (EDM) and plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) CIRP Ann. 2019;68:583–586. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2019.04.016. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

