Protealysin Targets the Bacterial Housekeeping Proteins FtsZ and RecA
- PMID: 36142700
- PMCID: PMC9505478
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810787
Protealysin Targets the Bacterial Housekeeping Proteins FtsZ and RecA
Abstract
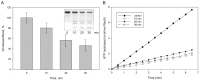
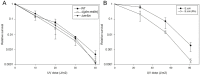
Serratia proteamaculans synthesizes the intracellular metalloprotease protealysin. This work was aimed at searching for bacterial substrates of protealysin among the proteins responsible for replication and cell division. We have shown that protealysin unlimitedly cleaves the SOS response protein RecA. Even 20% of the cleaved RecA in solution appears to be incorporated into the polymer of uncleaved monomers, preventing further polymerization and inhibiting RecA ATPase activity. Transformation of Escherichia coli with a plasmid carrying the protealysin gene reduces the bacterial UV survival up to 10 times. In addition, the protealysin substrate is the FtsZ division protein, found in both E. coli and Acholeplasma laidlawii, which is only 51% identical to E. coli FtsZ. Protealysin cleaves FtsZ at the linker between the globular filament-forming domain and the C-terminal peptide that binds proteins on the bacterial membrane. Thus, cleavage of the C-terminal segment by protealysin can lead to the disruption of FtsZ's attachment to the membrane, and thereby inhibit bacterial division. Since the protealysin operon encodes not only the protease, but also its inhibitor, which is typical for the system of interbacterial competition, we assume that in the case of penetration of protealysin into neighboring bacteria that do not synthesize a protealysin inhibitor, cleavage of FtsZ and RecA by protealysin may give S. proteamaculans an advantage in interbacterial competition.
Keywords: FtsZ; RecA; Serratia proteamaculans; interbacterial competition; protealysin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Balance between Protealysin and Its Substrate, the Outer Membrane Protein OmpX, Regulates Serratia proteamaculans Invasion.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 3;25(11):6159. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116159. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Filamentous actin is a substrate for protealysin, a metalloprotease of invasive Serratia proteamaculans.FEBS J. 2012 Jan;279(2):264-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08420.x. Epub 2011 Nov 30. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22077798
-
The protealysin operon encodes emfourin, a prototype of a novel family of protein metalloprotease inhibitors.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Feb 1;169:583-596. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.170. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33385454
-
Cleavage of the outer membrane protein OmpX by protealysin regulates Serratia proteamaculans invasion.FEBS Lett. 2020 Oct;594(19):3095-3107. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13897. Epub 2020 Aug 14. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 32748449
-
Bacterial Actin-Specific Endoproteases Grimelysin and Protealysin as Virulence Factors Contributing to the Invasive Activities of Serratia.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 4;21(11):4025. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114025. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32512842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Balance between Protealysin and Its Substrate, the Outer Membrane Protein OmpX, Regulates Serratia proteamaculans Invasion.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 3;25(11):6159. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116159. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RecA deletion disrupts protein homeostasis, leading to deamidation, oxidation, and impaired glycolysis in Cronobacter sakazakii.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Jan 31;91(1):e0197124. doi: 10.1128/aem.01971-24. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39745474 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

