Promising Application of D-Amino Acids toward Clinical Therapy
- PMID: 36142706
- PMCID: PMC9503604
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810794
Promising Application of D-Amino Acids toward Clinical Therapy
Abstract
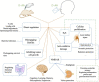
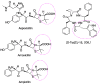
The versatile roles of D-amino acids (D-AAs) in foods, diseases, and organisms, etc., have been widely reported. They have been regarded, not only as biomarkers of diseases but also as regulators of the physiological function of organisms. Over the past few decades, increasing data has revealed that D-AAs have great potential in treating disease. D-AAs also showed overwhelming success in disengaging biofilm, which might provide promise to inhibit microbial infection. Moreover, it can effectively restrain the growth of cancer cells. Herein, we reviewed recent reports on the potential of D-AAs as therapeutic agents for treating neurological disease or tissue/organ injury, ameliorating reproduction function, preventing biofilm infection, and inhibiting cancer cell growth. Additionally, we also reviewed the potential application of D-AAs in drug modification, such as improving biostability and efficiency, which has a better effect on therapy or diagnosis.
Keywords: D-amino acid; protective effect; therapeutic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of local delivery of D-amino acids from biofilm-dispersive scaffolds on infection in contaminated rat segmental defects.Biomaterials. 2013 Oct;34(30):7533-43. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.06.026. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23831189
-
D-amino acid inhibits biofilm but not new bone formation in an ovine model.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Dec;473(12):3951-61. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4465-9. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 26201421 Free PMC article.
-
An in vitro study on the effect of free amino acids alone or in combination with nisin on biofilms as well as on planktonic bacteria of Streptococcus mutans.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 17;9(6):e99513. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099513. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24936873 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the inhibitory roles and mechanisms of D-amino acids in bacterial biofilms in medicine, industry, and agriculture.Microbiol Res. 2022 Oct;263:127107. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127107. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Microbiol Res. 2022. PMID: 35843196 Review.
-
D-amino acids in foods.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jan;104(2):555-574. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10264-9. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31832715 Review.
Cited by
-
Reparative and Antioxidant Effects of New Analogues of Immunomodulator Thymogen in Experimental Model of Liver Damage.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2023 Sep;175(5):700-703. doi: 10.1007/s10517-023-05929-5. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37861903
-
Chiral Amino Acids Mediate Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis of Human Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells Under Oxidative Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 15;25(24):13439. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413439. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769204 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective Effects of Thymogen Analogues in Hydrazine Hepatopathy in Rats.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2025 Apr;178(6):722-725. doi: 10.1007/s10517-025-06405-y. Epub 2025 May 29. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40442470
-
Effects of Gly-His-Lys-D-Ala Peptide on Skin Wound Regeneration Processes.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2024 Jan;176(3):411-416. doi: 10.1007/s10517-024-06035-w. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38345677
-
Biological and Analytical Perspectives on D-Amino Acids in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 9;18(5):705. doi: 10.3390/ph18050705. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430524 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

