Sustainable Production of Biosurfactant from Agro-Industrial Oil Wastes by Bacillus subtilis and Its Potential Application as Antioxidant and ACE Inhibitor
- PMID: 36142732
- PMCID: PMC9505973
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810824
Sustainable Production of Biosurfactant from Agro-Industrial Oil Wastes by Bacillus subtilis and Its Potential Application as Antioxidant and ACE Inhibitor
Abstract
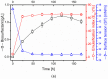
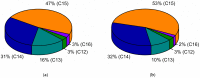
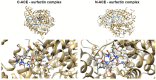
The microbial conversion of agro-industrial oil wastes into biosurfactants shows promise as a biomass refinery approach. In this study, Bacillus subtilis #309 was applied to produce surfactin using rapeseed and sunflower cakes, the most common oil processing side products in Europe. Studies of the chemical composition of the substrates were performed, to determine the feasibility of oil cakes for surfactin production. Initially, screening of proteolytic and lipolytic activity was performed to establish the capability of B. subtilis #309 for substrate utilization and hence effective surfactin production. B. subtilis #309 showed both proteolytic and lipolytic activity. The process of surfactin production was carefully analyzed by measurement of the surfactin concentration, pH, surface tension (ST) and emulsification index (E24). The maximal surfactin concentration in the sunflower and rapeseed cake medium reached 1.19 ± 0.03 and 1.45 ± 0.09 g/L, respectively. At the same time, a progressive decrease in the surface tension and increase in emulsification activity were observed. The results confirmed the occurrence of various surfactin homologues, while the surfactin C15 was the dominant one. Finally, the analysis of surfactin biological function exhibited antioxidant activity and significant angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory activity. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value for ACE inhibition was found to be 0.62 mg/mL for surfactin. Molecular docking of the surfactin molecule to the ACE domains confirmed its inhibitory activity against ACE. Several interactions, such as hydrophobic terms, hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions, were involved in the complex stabilization. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report describing the effect of a lipopeptide biosurfactant, surfactin, produced by B. subtilis for multifunctional properties in vitro, namely the ACE-inhibitory activity and the antioxidant properties, using different assays, such as 2,2-azinobis (3-ethyl-benzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS), 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP). Thus, the ACE-inhibitory lipopeptide biosurfactant shows promise to be used as a natural antihypertensive agent.
Keywords: ACE inhibitors; Bacillus subtilis; antioxidant; bioactive lipopeptide; biosurfactant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Production and optimization of surfactin produced from locally isolated Bacillus halotolerans grown on agro-industrial wastes and its antimicrobial efficiency.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Jun 3;24(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03338-w. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38831400 Free PMC article.
-
Sustainable Surfactin Production by Bacillus subtilis Using Crude Glycerol from Different Wastes.Molecules. 2021 Jun 8;26(12):3488. doi: 10.3390/molecules26123488. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34201182 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of dermal wound healing and in vitro antioxidant efficiency of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:878-891. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.084. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27750203
-
Bacillus licheniformis: The unexplored alternative for the anaerobic production of lipopeptide biosurfactants?Biotechnol Adv. 2022 Nov;60:108013. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.108013. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Biotechnol Adv. 2022. PMID: 35752271 Review.
-
Toxicity and applications of surfactin for health and environmental biotechnology.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2018;21(6-8):382-399. doi: 10.1080/10937404.2018.1564712. Epub 2019 Jan 7. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2018. PMID: 30614421 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements in biosurfactant production using agro-industrial waste for industrial and environmental applications.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 5;15:1357302. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1357302. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38374917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbially derived surfactants: an ecofriendly, innovative, and effective approach for managing environmental contaminants.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 26;12:1398210. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1398210. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39253704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant Properties of Biosurfactants: Multifunctional Biomolecules with Added Value in Formulation Chemistry.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 19;15(2):308. doi: 10.3390/biom15020308. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production and characterization of rhamnolipid biosurfactant from thermophilic Geobacillus stearothermophilus bacterium isolated from Uhud mountain.Front Microbiol. 2024 May 30;15:1358175. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1358175. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38873141 Free PMC article.
-
Biosurfactant Produced by Bacillus subtilis UCP 1533 Isolated from the Brazilian Semiarid Region: Characterization and Antimicrobial Potential.Microorganisms. 2025 Jul 1;13(7):1548. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13071548. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40732057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodríguez A., Gea T., Sánchez A., Font X. Agro-wastes and Inert Materials as Supports for the Production of Biosurfactants by Solid-state Fermentation. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2020;12:1963–1976. doi: 10.1007/s12649-020-01148-5. - DOI
-
- Rebello S., Asok A.K., Mundayoor S., Jisha M.S. Surfactants: Toxicity, remediation and green surfactants. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014;12:275–287. doi: 10.1007/s10311-014-0466-2. - DOI
-
- Drakontis C.E., Amin S. Biosurfactants: Formulations, properties, and applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;48:77–90. doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2020.03.013. - DOI
-
- De S., Malik S., Ghosh A., Saha R., Saha B. A review on natural surfactants. RSC Adv. 2015;5:65757–65767. doi: 10.1039/C5RA11101C. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

