Multiple Parallel Fusion Network for Predicting Protein Subcellular Localization from Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) Microscopy Images in Living Cells
- PMID: 36142736
- PMCID: PMC9504098
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810827
Multiple Parallel Fusion Network for Predicting Protein Subcellular Localization from Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) Microscopy Images in Living Cells
Abstract
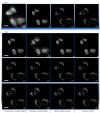
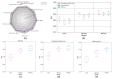
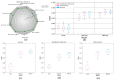
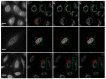
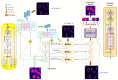
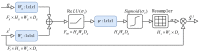
Stimulated Raman Scattering Microscopy (SRS) is a powerful tool for label-free detailed recognition and investigation of the cellular and subcellular structures of living cells. Determining subcellular protein localization from the cell level of SRS images is one of the basic goals of cell biology, which can not only provide useful clues for their functions and biological processes but also help to determine the priority and select the appropriate target for drug development. However, the bottleneck in predicting subcellular protein locations of SRS cell imaging lies in modeling complicated relationships concealed beneath the original cell imaging data owing to the spectral overlap information from different protein molecules. In this work, a multiple parallel fusion network, MPFnetwork, is proposed to study the subcellular locations from SRS images. This model used a multiple parallel fusion model to construct feature representations and combined multiple nonlinear decomposing algorithms as the automated subcellular detection method. Our experimental results showed that the MPFnetwork could achieve over 0.93 dice correlation between estimated and true fractions on SRS lung cancer cell datasets. In addition, we applied the MPFnetwork method to cell images for label-free prediction of several different subcellular components simultaneously, rather than using several fluorescent labels. These results open up a new method for the time-resolved study of subcellular components in different cells, especially cancer cells.
Keywords: deep learning; label-free live cell imaging; multiple parallel fusion network; nonlinear optical microscopy; protein subcellular localization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

