Myofibrillar Lattice Remodeling Is a Structural Cytoskeletal Predictor of Diaphragm Muscle Weakness in a Fibrotic mdx (mdx Cmah-/-) Model
- PMID: 36142754
- PMCID: PMC9500669
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810841
Myofibrillar Lattice Remodeling Is a Structural Cytoskeletal Predictor of Diaphragm Muscle Weakness in a Fibrotic mdx (mdx Cmah-/-) Model
Abstract
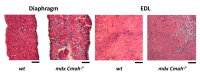
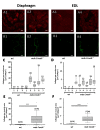
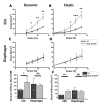
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a degenerative genetic myopathy characterized by complete absence of dystrophin. Although the mdx mouse lacks dystrophin, its phenotype is milder compared to DMD patients. The incorporation of a null mutation in the Cmah gene led to a more DMD-like phenotype (i.e., more fibrosis). Although fibrosis is thought to be the major determinant of 'structural weakness', intracellular remodeling of myofibrillar geometry was shown to be a major cellular determinant thereof. To dissect the respective contribution to muscle weakness, we assessed biomechanics and extra- and intracellular architecture of whole muscle and single fibers from extensor digitorum longus (EDL) and diaphragm. Despite increased collagen contents in both muscles, passive stiffness in mdx Cmah-/- diaphragm was similar to wt mice (EDL muscles were twice as stiff). Isometric twitch and tetanic stresses were 50% reduced in mdx Cmah-/- diaphragm (15% in EDL). Myofibrillar architecture was severely compromised in mdx Cmah-/- single fibers of both muscle types, but more pronounced in diaphragm. Our results show that the mdx Cmah-/- genotype reproduces DMD-like fibrosis but is not associated with changes in passive visco-elastic muscle stiffness. Furthermore, detriments in active isometric force are compatible with the pronounced myofibrillar disarray of the dystrophic background.
Keywords: cosine angle sum; multiphoton microscopy; muscular dystrophy; skeletal muscle; verniers density.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Contractile efficiency of dystrophic mdx mouse muscle: in vivo and ex vivo assessment of adaptation to exercise of functional end points.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017 Apr 1;122(4):828-843. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00776.2015. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017. PMID: 28057817
-
Collagen content does not alter the passive mechanical properties of fibrotic skeletal muscle in mdx mice.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 May 15;306(10):C889-98. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00383.2013. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24598364 Free PMC article.
-
Isometric resistance training increases strength and alters histopathology of dystrophin-deficient mouse skeletal muscle.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Feb 1;126(2):363-375. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00948.2018. Epub 2018 Dec 20. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019. PMID: 30571283 Free PMC article.
-
Current Translational Research and Murine Models For Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2016 Mar 3;3(1):29-48. doi: 10.3233/JND-150113. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2016. PMID: 27854202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of oxidative stress to pathology in diaphragm and limb muscles with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2013 Feb;34(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s10974-012-9330-9. Epub 2012 Oct 28. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2013. PMID: 23104273 Review.
Cited by
-
Bruno 1/CELF regulates splicing and cytoskeleton dynamics to ensure correct sarcomere assembly in Drosophila flight muscles.PLoS Biol. 2024 Apr 29;22(4):e3002575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002575. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38683844 Free PMC article.
-
Detyrosinated microtubule arrays drive myofibrillar malformations in mdx muscle fibers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Aug 25;11:1209542. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1209542. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37691825 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Matrix Proteomics: The mdx-4cv Mouse Diaphragm as a Surrogate for Studying Myofibrosis in Dystrophinopathy.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 12;13(7):1108. doi: 10.3390/biom13071108. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509144 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moxley R.T., Ashwal S., Pandya S., Connolly A., Florence J., Mathews K., Baumbach L., McDonald C., Sussman M., Wade C. Practice parameter: Corticosteroid treatment of Duchenne dystrophy: Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology. 2005;64:13–20. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000148485.00049.B7. - DOI - PubMed

