Inhibition of FGFR Signaling by Targeting FGF/FGFR Extracellular Interactions: Towards the Comprehension of the Molecular Mechanism through NMR Approaches
- PMID: 36142770
- PMCID: PMC9503799
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810860
Inhibition of FGFR Signaling by Targeting FGF/FGFR Extracellular Interactions: Towards the Comprehension of the Molecular Mechanism through NMR Approaches
Abstract
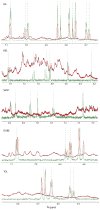
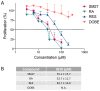
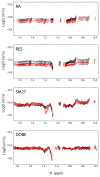
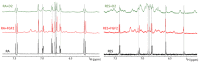
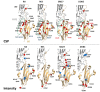
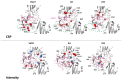
NMR-based approaches play a pivotal role in providing insight into molecular recognition mechanisms, affording the required atomic-level description and enabling the identification of promising inhibitors of protein-protein interactions. The aberrant activation of the fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2)/fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) signaling pathway drives several pathologies, including cancer development, metastasis formation, resistance to therapy, angiogenesis-driven pathologies, vascular diseases, and viral infections. Most FGFR inhibitors targeting the intracellular ATP binding pocket of FGFR have adverse effects, such as limited specificity and relevant toxicity. A viable alternative is represented by targeting the FGF/FGFR extracellular interactions. We previously identified a few small-molecule inhibitors acting extracellularly, targeting FGFR or FGF. We have now built a small library of natural and synthetic molecules that potentially act as inhibitors of FGF2/FGFR interactions to improve our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of inhibitory activity. Here, we provide a comparative analysis of the interaction mode of small molecules with the FGF2/FGFR complex and the single protein domains. DOSY and residue-level NMR analysis afforded insights into the capability of the potential inhibitors to destabilize complex formation, highlighting different mechanisms of inhibition of FGF2-induced cell proliferation.
Keywords: DOSY; NMR; allosteric inhibitors; dobesilate; fibroblast growth factor; resveratrol; rosmarinic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Krook M.A., Reeser J.W., Ernst G., Barker H., Wilberding M., Li G., Chen H.Z., Roychowdhury S. Fibroblast growth factor receptors in cancer: Genetic alterations, diagnostics, therapeutic targets and mechanisms of resistance. Br. J. Cancer. 2020;124:880–892. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01157-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

