Evaluation of Sodium Relaxation Times and Concentrations in the Achilles Tendon Using MRI
- PMID: 36142810
- PMCID: PMC9501448
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810890
Evaluation of Sodium Relaxation Times and Concentrations in the Achilles Tendon Using MRI
Abstract
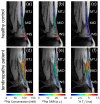
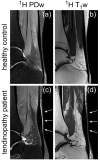
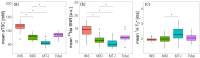
Sodium magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to evaluate the change in the proteoglycan content in Achilles tendons (ATs) of patients with different AT pathologies by measuring the 23Na signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). As 23Na SNR alone is difficult to compare between different studies, because of the high influence of hardware configurations and sequence settings on the SNR, we further set out to measure the apparent tissue sodium content (aTSC) in the AT as a better comparable parameter. Ten healthy controls and one patient with tendinopathy in the AT were examined using a clinical 3 Tesla (T) MRI scanner in conjunction with a dual tuned 1H/23Na surface coil to measure 23Na SNR and aTSC in their ATs. 23Na T1 and T2* of the AT were also measured for three controls to correct for different relaxation behavior. The results were as follows: 23Na SNR = 11.7 ± 2.2, aTSC = 82.2 ± 13.9 mM, 23Na T1 = 20.4 ± 2.4 ms, 23Na T2s* = 1.4 ± 0.4 ms, and 23Na T2l* = 13.9 ± 0.8 ms for the whole AT of healthy controls with significant regional differences. These are the first reported aTSCs and 23Na relaxation times for the AT using sodium MRI and may serve for future comparability in different studies regarding examinations of diseased ATs with sodium MRI.
Keywords: 23Na MRI; Achilles tendon; collagen; glycosaminoglycan; proteoglycan; sodium MRI; sodium concentration; sodium relaxation time; tendon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

