Influence of Bone Conduction Hearing Implantation on Health-Related Quality of Life for Patients with Chronic Otitis Media
- PMID: 36143094
- PMCID: PMC9502475
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11185449
Influence of Bone Conduction Hearing Implantation on Health-Related Quality of Life for Patients with Chronic Otitis Media
Abstract
Background: Chronic otitis media is a major public health burden that can result in a disabling hearing loss. Bone conduction hearing implants are an accepted form of hearing rehabilitation in these patients, but evidence supporting their usage typically comes from studies investigating mixed indications. The objective of our study was to examine how these devices impact health-related quality of life and hearing-disability in adult patients suffering from chronic otitis media.
Methods: Health Utilities Index-mark III (n = 10) and Speech Spatial and Qualities of Hearing-49 data (n = 6) were extracted for adult patients with chronic otitis media from an international hearing implant registry. Data were compared at baseline and at 12-month post-implantation with a bone conduction hearing implant.
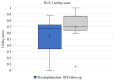
Results: Patients demonstrated a clinically relevant mean utility gain of 0.145 following implantation and clinically relevant mean improvement in global speech spatial and qualities of hearing score following implantation.
Conclusions: Bone conduction implantation was found to improve hearing and health-related quality of life and reduce hearing disability in a small cohort of patients with chronic otitis media. These data highlight the importance of providing appropriate hearing rehabilitation for individuals with chronic otitis media.
Keywords: bone conduction implant; cholesteatoma; chronic otitis media; hearing loss; hearing rehabilitation; quality of life; utility gain.
Conflict of interest statement
A.L. is a current employee of Cochlear Limited, a manufacturer and supplier of implantable hearing devices. V.G. is a former employee of Cochlear Limited.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

