Three-Dimensional Semantic Segmentation of Diabetic Retinopathy Lesions and Grading Using Transfer Learning
- PMID: 36143239
- PMCID: PMC9501488
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12091454
Three-Dimensional Semantic Segmentation of Diabetic Retinopathy Lesions and Grading Using Transfer Learning
Abstract
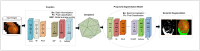
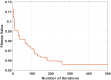
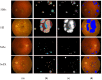
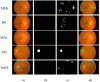
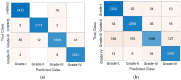
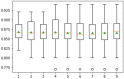
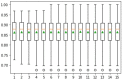
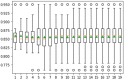
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a drastic disease. DR embarks on vision impairment when it is left undetected. In this article, learning-based techniques are presented for the segmentation and classification of DR lesions. The pre-trained Xception model is utilized for deep feature extraction in the segmentation phase. The extracted features are fed to Deeplabv3 for semantic segmentation. For the training of the segmentation model, an experiment is performed for the selection of the optimal hyperparameters that provided effective segmentation results in the testing phase. The multi-classification model is developed for feature extraction using the fully connected (FC) MatMul layer of efficient-net-b0 and pool-10 of the squeeze-net. The extracted features from both models are fused serially, having the dimension of N × 2020, amidst the best N × 1032 features chosen by applying the marine predictor algorithm (MPA). The multi-classification of the DR lesions into grades 0, 1, 2, and 3 is performed using neural network and KNN classifiers. The proposed method performance is validated on open access datasets such as DIARETDB1, e-ophtha-EX, IDRiD, and Messidor. The obtained results are better compared to those of the latest published works.
Keywords: DR; Messidor; convolutional neural network; deeplabv3; lesions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Improved diabetic retinopathy severity classification using squeeze-and-excitation and sparse light weight multi-level attention u-net with transfer learning from xception.Acta Diabetol. 2025 Jan;62(1):95-112. doi: 10.1007/s00592-024-02341-x. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Acta Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39060799
-
Localization and grading of NPDR lesions using ResNet-18-YOLOv8 model and informative features selection for DR classification based on transfer learning.Heliyon. 2024 May 9;10(10):e30954. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30954. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38779022 Free PMC article.
-
Combining transfer learning with retinal lesion features for accurate detection of diabetic retinopathy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 8;9:1050436. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1050436. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36425113 Free PMC article.
-
Explainable end-to-end deep learning for diabetic retinopathy detection across multiple datasets.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2020 Jul;7(4):044503. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.7.4.044503. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2020. PMID: 32904519 Free PMC article.
-
MSLF-Net: A Multi-Scale and Multi-Level Feature Fusion Net for Diabetic Retinopathy Segmentation.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 23;12(12):2918. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12122918. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552925 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prediction of Alzheimer's disease stages based on ResNet-Self-attention architecture with Bayesian optimization and best features selection.Front Comput Neurosci. 2024 Apr 25;18:1393849. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2024.1393849. eCollection 2024. Front Comput Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38725868 Free PMC article.
-
DRSegNet: A cutting-edge approach to Diabetic Retinopathy segmentation and classification using parameter-aware Nature-Inspired optimization.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 5;19(12):e0312016. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312016. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39637079 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Discrete Wavelet-Based Center-Symmetric Local Binary Pattern and Statistical Features.J Imaging Inform Med. 2025 Apr;38(2):1184-1211. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01243-2. Epub 2024 Sep 5. J Imaging Inform Med. 2025. PMID: 39237836 Free PMC article.
-
Level-set based adaptive-active contour segmentation technique with long short-term memory for diabetic retinopathy classification.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Dec 19;11:1286966. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1286966. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38169636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martinez-Murcia F.J., Ortiz A., Ramírez J., Górriz J.M., Cruz R. Deep residual transfer learning for automatic diagnosis and grading of diabetic retinopathy. Neurocomputing. 2021;452:424–434. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.04.148. - DOI
-
- Amin J., Sharif M., Yasmin M., Ali H., Fernandes S.L. A method for the detection and classification of diabetic retinopathy using structural predictors of bright lesions. J. Comput. Sci. 2017;19:153–164. doi: 10.1016/j.jocs.2017.01.002. - DOI
-
- Amin J., Anjum M.A., Malik M. Fused information of DeepLabv3+ and transfer learning model for semantic segmentation and rich features selection using equilibrium optimizer (EO) for classification of NPDR lesions. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022;249:108881. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108881. - DOI
-
- Wong T.Y., Sun J., Kawasaki R., Ruamviboonsuk P., Gupta N., Lansingh V.C., Maia M., Mathenge W., Moreker S., Muqit M.M., et al. Guidelines on Diabetic Eye Care: The International Council of Ophthalmology Recommendations for Screening, Follow-up, Referral, and Treatment Based on Resource Settings. Ophthalmology. 2018;125:1608–1622. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.04.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson C., Ferris F., Klein R., Lee P., Agardh C.D., Davis M., Dills D., Kampik A., Pararajasegaram R., Verdaguer J.T. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:1677–1682. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00475-5. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

