Predicting Local Failure after Partial Prostate Re-Irradiation Using a Dosiomic-Based Machine Learning Model
- PMID: 36143276
- PMCID: PMC9505150
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12091491
Predicting Local Failure after Partial Prostate Re-Irradiation Using a Dosiomic-Based Machine Learning Model
Abstract
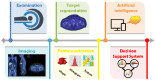
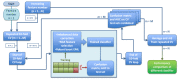
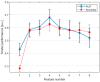
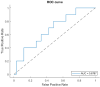
The aim of this study is to predict local failure after partial prostate re-irradiation for the treatment of isolated locally recurrent prostate cancer by using a machine learning classifier based on radiomic features from pre-treatment computed tomography (CT), positron-emission tomography (PET) and biological effective dose distribution (BED) of the radiotherapy plan. The analysis was conducted on a monocentric dataset of 43 patients with evidence of isolated intraprostatic recurrence of prostate cancer after primary external beam radiotherapy. All patients received partial prostate re-irradiation delivered by volumetric modulated arc therapy. The gross tumor volume (GTV) of each patient was manually contoured from planning CT, choline-PET and dose maps. An ensemble machine learning pipeline including unbalanced data correction and feature selection was trained using the radiomic and dosiomic features as input for predicting occurrence of local failure. The model performance was assessed using sensitivity, specificity, accuracy and area under receiver operating characteristic curves of the score function in 10-fold cross validation repeated 100 times. Local failure was observed in 13 patients (30%), with a median time to recurrence of 36.7 months (range = 6.1-102.4 months). A four variables ensemble machine learning model resulted in accuracy of 0.62 and AUC 0.65. According to our results, a dosiomic machine learning classifier can predict local failure after partial prostate re-irradiation.
Keywords: dosiomics; machine learning; partial prostate re-irradiation; prostate cancer; radiomics; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zelefsky M.J., Kollmeier M., Cox B., Fidaleo A., Sperling D., Pei X., Carver B., Coleman J., Lovelock M., Hunt M. Improved Clinical Outcomes with High-Dose Image Guided Radiotherapy Compared with Non-IGRT for the Treatment of Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012;84:125–129. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.11.047. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goy B.W., Burchette R., Soper M.S., Chang T., Cosmatos H.A. Ten-Year Treatment Outcomes of Radical Prostatectomy Vs External Beam Radiation Therapy Vs Brachytherapy for 1503 Patients with Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer. Urology. 2020;136:180–189. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2019.09.040. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jansen B.H.E., van Leeuwen P.J., Wondergem M., van der Sluis T.M., Nieuwenhuijzen J.A., Knol R.J.J., van Moorselaar R.J.A., van der Poel H.G., Oprea-Lager D.E., Vis A.N. Detection of Recurrent Prostate Cancer Using Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography in Patients Not Meeting the Phoenix Criteria for Biochemical Recurrence After Curative Radiotherapy. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021;4:821–825. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2020.01.002. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

