A Meta-Analysis on the Effectiveness of Sertaconazole 2% Cream Compared with Other Topical Therapies for Seborrheic Dermatitis
- PMID: 36143325
- PMCID: PMC9501484
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12091540
A Meta-Analysis on the Effectiveness of Sertaconazole 2% Cream Compared with Other Topical Therapies for Seborrheic Dermatitis
Abstract
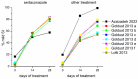
Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) is a relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that affects the seborrheic areas of the body. Its etiology is not completely elucidated; however, the link between disease exacerbations and the proliferation of Malassezia spp., along with the good response to antifungal agents, indicate the role of fungi in its pathophysiology. Sertaconazole nitrate is a relatively new imidazole antifungal agent with a particular structure, consisting in a benzothiophene ring similar to the indole ring of tryptophan, and it acts mainly through the inhibition of ergosterol synthesis and the formation of pores in the fungal cell membrane. The aim of our study was to evaluate the efficiency of sertaconazole 2% cream compared with other topical treatments in patients with SD. We performed an extensive literature search by browsing the PubMed database with the keyword combination "sertaconazole AND seborrheic dermatitis AND clinical trial", which retrieved eight controlled clinical trials evaluating the effects of sertaconazole in SD. All of the clinical trials included a standard scoring index (SI). At 28 days since the beginning of the treatment, the sertaconazole regimen was associated with a significantly higher percentage of patients with mild SI and a lower percentage of patients with moderate or severe SI (odds ratio 0.51) than the other investigated treatments-hydrocortisone, ketoconazole, clotrimazole, metronidazole, pimecrolimus, and tacrolimus (odds ratio 1.95). In conclusion, treatment with sertaconazole 2% cream may represent an efficient alternative therapy for patients with SD.
Keywords: Malassezia; seborrheic dermatitis; sertaconazole; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis: the efficiency of sertaconazole 2% cream vs. tacrolimus 0.03% cream.Ann Parasitol. 2013;59(2):73-7. Ann Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 24171300 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis, comparison of sertaconazole 2% cream versus ketoconazole 2% cream.J Dermatolog Treat. 2013 May 6. doi: 10.3109/09546634.2013.777154. Online ahead of print. J Dermatolog Treat. 2013. PMID: 23441833
-
Double blind study of sertaconazole 2% cream vs. clotrimazole 1% cream in treatment of seborrheic dermatitis.Ann Parasitol. 2013;59(1):25-9. Ann Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23829055 Clinical Trial.
-
Sertaconazole: a review of its use in the management of superficial mycoses in dermatology and gynaecology.Drugs. 2009;69(3):339-59. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969030-00009. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19275277 Review.
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Pimecrolimus in Patients With Facial Seborrheic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.Cureus. 2022 Aug 2;14(8):e27622. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27622. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36072203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Child and Adult Seborrheic Dermatitis: A Narrative Review of the Current Treatment Landscape.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025 Mar;15(3):599-613. doi: 10.1007/s13555-025-01351-z. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 39953371 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

