Genome Organization and Comparative Evolutionary Mitochondriomics of Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Biotype 4 Using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
- PMID: 36143326
- PMCID: PMC9506247
- DOI: 10.3390/life12091289
Genome Organization and Comparative Evolutionary Mitochondriomics of Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Biotype 4 Using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Abstract
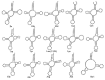
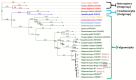
Nilaparvata lugens is the main rice pest in India. Until now, the Indian N. lugens mitochondrial genome has not been sequenced, which is a very important basis for population genetics and phylogenetic evolution studies. An attempt was made to sequence two examples of the whole mitochondrial genome of N. lugens biotype 4 from the Indian population for the first time. The mitogenomes of N. lugens are 16,072 and 16,081 bp long with 77.50% and 77.45% A + T contents, respectively, for both of the samples. The mitochondrial genome of N. lugens contains 37 genes, including 13 protein-coding genes (PCGs) (cox1-3, atp6, atp8, nad1-6, nad4l, and cob), 22 transfer RNA genes, and two ribosomal RNA (rrnS and rrnL) subunits genes, which are typical of metazoan mitogenomes. However, both samples of N. lugens mitogenome in the present study retained one extra copy of the trnC gene. Additionally, we also found 93 bp lengths for the atp8 gene in both of the samples, which were 60-70 bp less than that of the other sequenced mitogenomes of hemipteran insects. The phylogenetic analysis of the 19 delphacids mitogenome dataset yielded two identical topologies when rooted with Ugyops sp. in one clade, and the remaining species formed another clade with P. maidis and M. muiri being sisters to the remaining species. Further, the genus Nilaparvata formed a separate subclade with the other genera (Sogatella, Laodelphax, Changeondelphax, and Unkanodes) of Delphacidae. Additionally, the relationship among the biotypes of N. lugens was recovered as the present study samples (biotype-4) were separated from the three biotypes reported earlier. The present study provides the reference mitogenome for N. lugens biotype 4 that may be utilized for biotype differentiation and molecular-aspect-based future studies of N. lugens.
Keywords: NGS; mitochondria; phloem feeder; phylogeny; sucking pest.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Pandi G., Chander S., Singh M.P. Impact of elevated CO2 on rice brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stal.) Indian J. Entomol. 2017;79:82–85. doi: 10.5958/0974-8172.2017.00018.9. - DOI
-
- Jena M., Govindharaj G.-P.-P., Adak T., Rath P., Gowda G B., Patil N., Prasanthi G., Mohapatra S. Paradigm shift of insect pests in rice ecosystem and their management strategy. ORYZA-An Int. J. Rice. 2018;55:82–89. doi: 10.5958/2249-5266.2018.00010.3. - DOI
-
- Guru-Pirasanna-Pandi G., Chander S., Pal M., Soumia P.S. Impact of elevated CO2 on Oryza sativa phenology and brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) population. Curr. Sci. 2018;114:1767–1777. doi: 10.18520/cs/v114/i08/1767-1777. - DOI
-
- Anant A.K., Guru-Pirasanna-Pandi G., Jena M., Chandrakar G., Chidambaranathan P., Raghu S., Gowda G.B., Annamalai M., Patil N., Adak T., et al. Genetic dissection and identification of candidate genes for brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Delphacidae: Hemiptera) resistance in farmers’ varieties of rice in Odisha. Crop Prot. 2021;144:105600. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2021.105600. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

