Evaluation of the Upper Arch Morphological Changes after Two Different Protocols of Expansion in Early Mixed Dentition: Rapid Maxillary Expansion and Invisalign® First System
- PMID: 36143360
- PMCID: PMC9502768
- DOI: 10.3390/life12091323
Evaluation of the Upper Arch Morphological Changes after Two Different Protocols of Expansion in Early Mixed Dentition: Rapid Maxillary Expansion and Invisalign® First System
Abstract
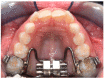
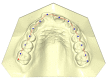
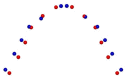
Background: The objective of this retrospective study was to analyze the morphological changes of the upper arch after two protocols of expansion, the Invisalign® First system and rapid maxillary expansion (RME), in mixed dentition by means of geometric morphometric analysis (GMM). Methods: Digital dental casts of 32 children treated either with RME (RME group: 17 subjects; mean age 8.1 years) or the First system (First group: subjects; mean age 8.4 years) were collected. For both the RG and FG, pre-(T1) and post-treatment(T2) digital models were created. A total of 14 landmarks were digitized and GMM was applied. Procrustes analysis and principal component analysis (PCA) were performed. Results: The PC1 resulting from the T2-T1 comparison in the RG g showed statistically significant morphological changes in the posterior region of the upper arch shape, without significant variations in the anterior region. The comparison of the T2-T1 changes in the FG showed an increase in the transverse dimension at the level of the canine and the first deciduous molar widths, with morphological variation in the anterior region due to frontal teeth alignment. Conclusions: The First system induced shape modifications of the upper arch during expansion in contrast to RME. The FG presented an improvement in the maxillary arch shape, while the RG maintained the initial triangular shape.
Keywords: Invisalign® First system; RME; geometric morphometrics; maxillary expansion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treatment effects after maxillary expansion using invisalign first system vs. acrylic splint expander in mixed dentition: a prospective cohort study.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Aug 27;23(1):598. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03312-4. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37635237 Free PMC article.
-
Upper arch dimensional changes with clear aligners in the early mixed dentition : A prospective study.J Orofac Orthop. 2023 Jan;84(1):33-40. doi: 10.1007/s00056-021-00332-z. Epub 2021 Sep 3. J Orofac Orthop. 2023. PMID: 34477905 English.
-
Palatal vault morphometric analysis of the effects of two early orthodontic treatments in anterior open bite growing subjects: a controlled clinical study.BMC Oral Health. 2021 Oct 11;21(1):514. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01886-5. BMC Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 34635118 Free PMC article.
-
Dento-skeletal effects produced by rapid versus slow maxillary expansion using fixed jackscrew expanders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Orthod. 2021 Jun 8;43(3):301-312. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjaa086. Eur J Orthod. 2021. PMID: 33950178
-
The effect of maxillary protraction, with or without rapid palatal expansion, on airway dimensions: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2020 Dec;21(4):262-270. doi: 10.23804/ejpd.2020.21.04.2. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2020. PMID: 33337900
Cited by
-
Dimensional changes in the palate associated with Invisalign First System: a pilot study.Angle Orthod. 2023 Sep 1;93(5):524-530. doi: 10.2319/110422-755.1. Angle Orthod. 2023. PMID: 37052464 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Class II elastics on lower incisors during treatment with clear aligners vs. fixed appliance: a randomized clinical trial.Front Dent Med. 2025 Jul 10;6:1613037. doi: 10.3389/fdmed.2025.1613037. eCollection 2025. Front Dent Med. 2025. PMID: 40708614 Free PMC article.
-
Vertical and transverse treatment effects of Invisalign First system compared to Hyrax maxillary expanders with fixed appliances in mixed dentition patients.Angle Orthod. 2024 Sep 1;94(5):496-503. doi: 10.2319/121023-818.1. Angle Orthod. 2024. PMID: 39230021 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between transverse and sagittal dimensions in early stage: a retrospective study between patients treated with clear aligners and untreated patients.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Apr 11;25(1):548. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05893-8. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40217238 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Crowding Associated with Lower Canine Premature Resorption: Interceptive Treatment with Clear Aligners-A Pilot Study.Children (Basel). 2024 Apr 8;11(4):451. doi: 10.3390/children11040451. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paoloni V., Giuntini V., Lione R., Nieri M., Barone V., Merlo M.M., Mazza F., Passaleva S., Cozza P., Franchi L. Comparison of the dento-skeletal effects produced by Leaf expander versus rapid maxillary expander in prepubertal patients: A two-center randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Orthod. 2021;44:163–169. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjab035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lione R., Pavoni C., Laganà G., Fanucci E., Ottria L., Cozza P. Rapid maxillary expansion: Effects on palatal area in-vestigated by computed tomography in growing subjects. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2012;13:215–218. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

