A Turf-Based Feature Selection Technique for Predicting Factors Affecting Human Health during Pandemic
- PMID: 36143404
- PMCID: PMC9502730
- DOI: 10.3390/life12091367
A Turf-Based Feature Selection Technique for Predicting Factors Affecting Human Health during Pandemic
Abstract
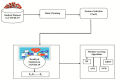
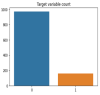
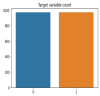
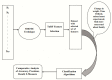
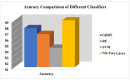
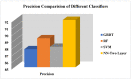
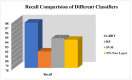
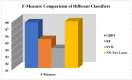
Worldwide, COVID-19 is a highly contagious epidemic that has affected various fields. Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and particular feature selection approaches, this study evaluates the aspects affecting the health of students throughout the COVID-19 lockdown time. The research presented in this paper plays a vital role in indicating the factor affecting the health of students during the lockdown in the COVID-19 pandemic. The research presented in this article investigates COVID-19's impact on student health using feature selections. The Filter feature selection technique is used in the presented work to statistically analyze all the features in the dataset, and for better accuracy. ReliefF (TuRF) filter feature selection is tuned and utilized in such a way that it helps to identify the factors affecting students' health from a benchmark dataset of students studying during COVID-19. Random Forest (RF), Gradient Boosted Decision Trees (GBDT), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and 2- layer Neural Network (NN), helps in identifying the most critical indicators for rapid intervention. Results of the approach presented in the paper identified that the students who maintained their weight and kept themselves busy in health activities in the pandemic, such student's remained healthy through this pandemic and study from home in a positive manner. The results suggest that the 2- layer NN machine-learning algorithm showed better accuracy (90%) to predict the factors affecting on health issues of students during COVID-19 lockdown time.
Keywords: COVID-19; artificial intelligence; feature selection; human health; lock down; mental stress; pandemic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Seminal quality prediction using data mining methods.Technol Health Care. 2014;22(4):531-45. doi: 10.3233/THC-140816. Technol Health Care. 2014. PMID: 24898862
-
E-learningDJUST: E-learning dataset from Jordan university of science and technology toward investigating the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on education.Neural Comput Appl. 2023;35(16):11481-11495. doi: 10.1007/s00521-021-06712-1. Epub 2021 Nov 13. Neural Comput Appl. 2023. PMID: 34803236 Free PMC article.
-
An Explainable Machine Learning Approach for COVID-19's Impact on Mood States of Children and Adolescents during the First Lockdown in Greece.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;10(1):149. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10010149. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052311 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Student Performance from Online Engagement Activities Using Novel Statistical Features.Arab J Sci Eng. 2022;47(8):10225-10243. doi: 10.1007/s13369-021-06548-w. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Arab J Sci Eng. 2022. PMID: 35070634 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and predicting factors of perceived stress among Bangladeshi university students using machine learning algorithms.J Health Popul Nutr. 2021 Nov 27;40(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s41043-021-00276-5. J Health Popul Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34838133 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Deep Dive into the Nexus between Digital Health and Life Sciences Amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Editorial Expedition.Life (Basel). 2023 May 10;13(5):1154. doi: 10.3390/life13051154. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37240800 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

