Renessans Helps in Early Clearance of SARS-CoV-2: In-Vivo Activity of the Iodine Complex in Rhesus macaque
- PMID: 36143459
- PMCID: PMC9571793
- DOI: 10.3390/life12091424
Renessans Helps in Early Clearance of SARS-CoV-2: In-Vivo Activity of the Iodine Complex in Rhesus macaque
Abstract
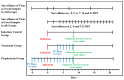
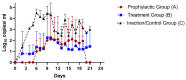
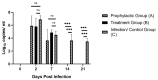
Iodine complexes have known antimicrobial properties along with reported in-vitro antiviral activity for several viruses. Renessans is one such product with iodine complexes and ascorbic acid. The present study was designed to determine its efficacy for SARS-CoV-2 in Rhesus macaque. Rhesus macaque were assigned to: A) prophylactic group (n = 3), (B) treatment group (n = 3), (C) infection control group (n = 4), and (D) negative control group (n = 4). Groups A, B, and C were challenged with 2 × 106 TCID of SARS-CoV-2. The prophylactic group (A) was administered Renessans from 5 days before infection till 8 days postinfection (DPI). The treatment group (B) was administered Renessans from 3 till 8 DPI. Group C was administered water-insoluble fractions only. Nasal swabs from all monkeys of groups A, B, and C remained positive for SARS-CoV-2 till 2 and 7 DPI, while the swabs became negative for groups A and B at 14 DPI. Likewise, fecal matter of monkeys in group A returned negative results during the experiment, while that of group B had significantly decreased viral load (101.5 genome copies/mL) compared to group C (103 genome copies/mL). Hence, it is concluded that Renessans has in-vivo SARS-CoV-2 activity and may result in early clearance of SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; animal trial; antiviral; coronavirus; iodine compound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An in vitro antiviral activity of iodine complexes against SARS-CoV-2.Arch Microbiol. 2021 Sep;203(7):4743-4749. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02430-3. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Arch Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34136927 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral Efficacies of FDA-Approved Drugs against SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Ferrets.mBio. 2020 May 22;11(3):e01114-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01114-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32444382 Free PMC article.
-
Human Nasal Epithelial Cells Sustain Persistent SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vitro, despite Eliciting a Prolonged Antiviral Response.mBio. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):e0343621. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03436-21. Epub 2022 Jan 18. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35038898 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing povidone-iodine to reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission: a narrative review.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):1488-1499. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2076902. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 35594333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 28;7(7):CD015017. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015017.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 21;6:CD015017. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015017.pub3. PMID: 34318930 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Patterns of Dietary Supplement Use during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Poland: Focus on Vitamin D and Magnesium.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 24;16(19):3225. doi: 10.3390/nu16193225. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39408194 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 20;13(3):834. doi: 10.3390/life13030834. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Statement on the Second Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee Regarding the Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) [(accessed on 18 August 2020)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-...
-
- Worldometer Coronavirus Cases. [(accessed on 18 July 2020)]. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

