Usnic Acid Isolated from Usnea antarctica (Du Rietz) Reduced In Vitro Angiogenesis in VEGF- and bFGF-Stimulated HUVECs and Ex Ovo in Quail Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay
- PMID: 36143480
- PMCID: PMC9503005
- DOI: 10.3390/life12091444
Usnic Acid Isolated from Usnea antarctica (Du Rietz) Reduced In Vitro Angiogenesis in VEGF- and bFGF-Stimulated HUVECs and Ex Ovo in Quail Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay
Abstract
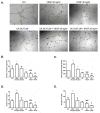
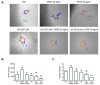
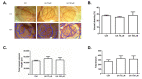
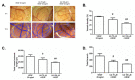
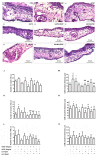
Natural products include a diverse set of compounds of drug discovery that are currently being actively used to target tumor angiogenesis. In the present study, we evaluated the anti-angiogenic activities of secondary metabolite usnic acid isolated from Usena antarctica. We investigated the in vitro effects on proliferation, migration, and tube formation of VEGF- and bFGF-stimulated HUVECs. Ex ovo anti-angiogenic activity was evaluated using the CAM assay. Our findings demonstrated that usnic acid in the concentration of 33.57 µM inhibited VEGF (25 ng/mL) and bFGF (30 ng/mL)-induced HUVECs proliferation, migration, and tube formation. The ex ovo CAM model was used to confirm the results obtained from in vitro studies. VEGF- and bFGF-induced vessel formation was inhibited by usnic acid after 72 h in over 2-fold higher concentrations compared to in vitro. Subsequently, histological sections of affected chorioallantoic membranes were stained with hematoxylin-eosin and alcian blue to determine the number and diameter of vessels as well as the thickness of the individual CAM layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm). Usnic acid was able to suppress the formation of VEGF- and bFGF-induced vessels with a diameter of less than 100 μm, which was demonstrated by the reduction of mesoderm thickness as well.
Keywords: CAM; HUVECs; VEGF; angiogenesis; bFGF; usnic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Antiangiogenic Activity of n-hexane Insoluble Fraction and Its Tylophorine Component from Ficus septica Leaves in Chicken Chorioallantoic Membrane Induced by bFGF.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Jan 1;24(1):75-80. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.1.75. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 36708554 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of tecogalan sodium on angiogenesis in vitro by choroidal endothelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995 May;36(6):1076-83. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995. PMID: 7537258
-
Novel approach for biomaterial assessment: utilizing the Ex Ovo quail cam assay for biocompatibility pre-screening.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Nov 21;49(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10574-y. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 39570443 Free PMC article.
-
Daphnetin inhibits TNF-α and VEGF-induced angiogenesis through inhibition of the IKKs/IκBα/NF-κB, Src/FAK/ERK1/2 and Akt signalling pathways.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Oct;43(10):939-50. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12608. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27297262
-
Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay as Model for Angiogenesis in Tissue Engineering: Focus on Stem Cells.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020 Dec;26(6):519-539. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2020.0048. Epub 2020 May 1. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020. PMID: 32220219 Review.
Cited by
-
Screening Evaluation of Antiproliferative, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity of Lichen Extracts and Secondary Metabolites In Vitro.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 30;12(3):611. doi: 10.3390/plants12030611. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771693 Free PMC article.
-
BRAF inhibitor candidate molecule usnic acid might use both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis.Turk J Med Sci. 2024 Aug 9;54(5):1116-1126. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5890. eCollection 2024. Turk J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39473730 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo antiangiogenic effect of nimbolide, trans-chalcone and piperine for use against glioblastoma.BMC Cancer. 2023 Nov 30;23(1):1173. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11625-4. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38036978 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling Novel Phytochemicals and Anticholinesterase Activity in Irish Cladonia portentosa.Molecules. 2023 May 17;28(10):4145. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104145. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241886 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-angiogenic Potential of Trans-chalcone in an In Vivo Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane Model: An ATP Antagonist to VEGFR with Predicted Blood-brain Barrier Permeability.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2024;22(2):187-211. doi: 10.2174/0118715257250417231019102501. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37936455
References
-
- Hurwitz H., Fehrenbacher L., Novotny W., Cartwright T., Hainsworth J., Heim W., Berlin J., Baron A., Griffing S., Holmgren E., et al. Bevacizumab plus Irinotecan, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2335–2342. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032691. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- VEGA 1/0653/19/Grant Agency of the Ministry of the Education, Science, Research, and Sport of the Slovak Republic
- VEGA 1/0071/21/Grant Agency of the Ministry of the Education, Science, Research, and Sport of the Slovak Republic
- KEGA 006UPJŠ-4/2020/Grant Agency of the Ministry of the Education, Science, Research, and Sport of the Slovak Republic
- ITMS2014+: 313011V455/Open scientific community for modern interdisciplinary research in medicine (OPENMED),supported by the Operational Programme Integrated Infrastructure, funded by the ERDF.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

