A Combination of Two Probiotics, Lactobacillus sporogenes and Clostridium butyricum, Inhibits Colon Cancer Development: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 36144294
- PMCID: PMC9506018
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10091692
A Combination of Two Probiotics, Lactobacillus sporogenes and Clostridium butyricum, Inhibits Colon Cancer Development: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
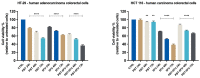
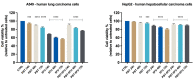
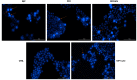
Cancer remains a leading cause of death worldwide and, even though several advances have been made in terms of specific treatment, the late-stage detection and the associated side effects of the conventional drugs sustain the search for better treatment alternatives. Probiotics are live microorganisms that have been proven to possess numerous health benefits for human hosts, including anticancer effects. In the present study, the in vitro effect of the association of two probiotic strains (PBT), Lactobacillus sporogenes and Clostridium butyricum, were tested against colon (HT-29 and HCT 116), lung (A549), and liver (HepG2) cancer cell lines, alone or in combination with 5-fluorouracil (5FU). Moreover, the underlying mechanism of PBT and PBT-5FU against the HT-29 cell line was evaluated using the Hoechst 33342 staining, revealing characteristic apoptotic modifications, such as chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation, and membrane blebbing. Furthermore, the increase in the expression of pro-apoptotic Bax, Bid, Bad, and Bak proteins and the inhibition of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL proteins were recorded. Collectively, these findings suggest that the two strains of probiotic bacteria, alone or in association with 5FU, induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells and may serve as a potential anticancer treatment.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; Clostridium butyricum; Lactobacillus sporogenes; apoptosis; colon cancer; liver cancer; lung cancer; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of cell death events induced by anti-neoplastic drugs cisplatin, paclitaxel and 5-fluorouracil on human hepatoma cell lines: Possible mechanisms of cell resistance.Biomed Pharmacother. 2007 Jul;61(6):347-55. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2007.02.007. Epub 2007 Mar 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17399942
-
Therapeutic effects of probiotic Clostridium butyricum WZ001 on bacterial vaginosis in mice.J Appl Microbiol. 2019 Aug;127(2):565-575. doi: 10.1111/jam.14329. Epub 2019 Jun 7. J Appl Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31102489
-
Lactobacillus acidophilus and Clostridium butyricum ameliorate colitis in murine by strengthening the gut barrier function and decreasing inflammatory factors.Benef Microbes. 2018 Sep 18;9(5):775-787. doi: 10.3920/BM2017.0035. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Benef Microbes. 2018. PMID: 30014710
-
Anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic and anti-oxidative activity of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains: A review of mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(21):3456-3467. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1494539. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30010390 Review.
-
Should Lactobacillus sporogenes and Bacillus coagulans have a future?J Chemother. 2009 Aug;21(4):371-7. doi: 10.1179/joc.2009.21.4.371. J Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19622453 Review.
Cited by
-
An Update on the Pivotal Roles of Probiotics, Their Components, and Metabolites in Preventing Colon Cancer.Foods. 2023 Oct 9;12(19):3706. doi: 10.3390/foods12193706. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37835359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health-Promoting and Functional Properties of Fermented Milk Beverages with Probiotic Bacteria in the Prevention of Civilization Diseases.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 24;17(1):9. doi: 10.3390/nu17010009. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39796443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer effect of a combinatorial treatment of 5-fluorouracil and cell extract of some probiotic lactobacilli strains isolated from camel milk on colorectal cancer cells.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2024 Dec 20. doi: 10.1007/s12223-024-01228-2. Online ahead of print. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2024. PMID: 39702737
-
Tumor-targeted induction of intrinsic apoptosis in colon cancer cells by Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jun;50(6):5345-5354. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08445-x. Epub 2023 May 8. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37155013
-
Clostridium butyricum, a future star in sepsis treatment.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Dec 6;14:1484371. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1484371. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39711782 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cancer. [(accessed on 21 June 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer.
-
- Peng M., Tabashsum Z., Anderson M., Truong A., Houser A.K., Padilla J., Akmel A., Bhatti J., Rahaman S.O., Biswas D. Effectiveness of probiotics, prebiotics, and prebiotic-like components in common functional foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020;19:1908–1933. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12565. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

