Epidemiological and Serological Analysis of a SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak in a Nursing Home: Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Enhanced Neutralizing Immunity Following Breakthrough Infection
- PMID: 36144413
- PMCID: PMC9505589
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10091809
Epidemiological and Serological Analysis of a SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak in a Nursing Home: Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Enhanced Neutralizing Immunity Following Breakthrough Infection
Abstract
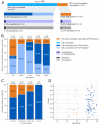
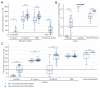
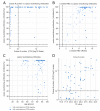
Background: Despite a vaccination rate of 82.0% (n = 123/150), a SARS-CoV-2 (Alpha) outbreak with 64.7% (n = 97/150) confirmed infections occurred in a nursing home in Bavaria, Germany. Objective: the aim of this retrospective cohort study was to examine the effects of the Corminaty vaccine in a real-life outbreak situation and to obtain insights into the antibody response to both vaccination and breakthrough infection. Methods: the antibody status of 106 fully vaccinated individuals (54/106 breakthrough infections) and epidemiological data on all 150 residents and facility staff were evaluated. Results: SARS-CoV-2 infections (positive RT-qPCR) were detected in 56.9% (n = 70/123) of fully vaccinated, compared to 100% (n = 27/27) of incompletely or non-vaccinated individuals. The proportion of hospitalized and deceased was 4.1% (n = 5/123) among fully vaccinated and therewith lower compared to 18.5% (n = 5/27) hospitalized and 11.1% (n = 3/27) deceased among incompletely or non-vaccinated. Ct values were significantly lower in incompletely or non-vaccinated (p = 0.02). Neutralizing antibodies were detected in 99.1% (n = 105/106) of serum samples with significantly higher values (p < 0.001) being measured post-breakthrough infection. α-N-antibodies were detected in 37.7% of PCR positive but not in PCR negative individuals. Conclusion: Altogether, our data indicate that SARS-CoV-2 vaccination does provide protection against infection, severe disease progression and death with regards to the Alpha variant. Nonetheless, it also shows that infection and transmission are possible despite full vaccination. It further indicates that breakthrough infections can significantly enhance α-S- and neutralizing antibody responses, indicating a possible benefit from booster vaccinations.
Keywords: Comirnaty® COVID-19 vaccine; SARS-CoV-2 Alpha variant; SARS-CoV-2 antibodies; breakthrough infection; epidemiology; neutralizing antibodies; nursing home; outbreak; serology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Rotondo J.C., Martini F., Maritati M., Mazziotta C., Di Mauro G., Lanzillotti C., Barp N., Gallerani A., Tognon M., Contini C. SARS-CoV-2 Infection: New Molecular, Phylogenetic, and Pathogenetic Insights. Efficacy of Current Vaccines and the Potential Risk of Variants. Viruses. 2021;13:1687. doi: 10.3390/v13091687. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pineles L., Perencevich E.N., Roghmann M.C., Gupta K., Cadena J., Baracco G., Pfeiffer C.D., Forrest G., Bradley S.F., Crnich C., et al. Frequency of nursing home resident contact with staff, other residents, and the environment outside resident rooms. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2019;40:815–816. doi: 10.1017/ice.2019.117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chudasama D.Y., Milbourn H., Nsonwu O., Senyah F., Florence I., Cook B., Marchant E., Blomquist P.B., Flannagan J., Dabrera G., et al. Penetration and impact of COVID-19 in long term care facilities in England: Population surveillance study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021;50:1804–1813. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyab176. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paranthaman K., Allen H., Chudasama D., Verlander N.Q., Sedgwick J. Case-control study to estimate odds of death within 28 days of positive test for SARS-CoV-2 prior to vaccination for residents of long-term care facilities in England, 2020–2021. J. Epidemiol. Community Health. 2021;76:428–434. doi: 10.1136/jech-2021-218135. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

