Genetic Diversity of Pectobacterium spp. on Potato in Serbia
- PMID: 36144442
- PMCID: PMC9503840
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10091840
Genetic Diversity of Pectobacterium spp. on Potato in Serbia
Abstract
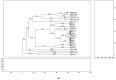
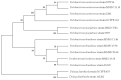
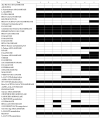
Pectobacterium is a diverse genus which comprises of multiple destructive bacterial species which cause soft rot/blackleg/wilt disease complex in a wide variety of crops by employing high levels of virulence factors. During the 2018, 2019 and 2020 potato growing seasons, numerous outbreaks of bacterial wilt, stem blackleg and tuber soft rot were recorded, and symptomatic plant samples from ten localities in the Province of Vojvodina (Serbia) were collected and analysed. Bacterial soft-rot pathogens were detected in 63 samples using genus and species-specific primers. Through 16S rRNA Sanger sequencing of 19 representative isolates, the identity of P. brasiliense (73.7%), P. punjabense (15.8%), and P. carotovorum (10.5%) species were revealed. To further validate the identification, genotypic profiling of Pectobacterium strains using rep-PCR (ERIC, BOX, REP) was conducted for 25 selected isolates and the phylogenetic assessment based on four selected housekeeping genes (gyrA, recA, rpoA, and rpoS). Physiological and biochemical properties were analysed using basic microbiological tests and VITEK® 2 GN card, and pathogenicity was confirmed on cv. VR808 and cv. Desiree potato tubers and plants. This study confirmed the distinctiveness of the newly described P. punjabense in Serbia as well as the high diversity of Pectobacterium brasiliense and Pectobacterium carotovorum species in Serbia.
Keywords: MLSA; Pectobacteriaceae; Pectobacterium punjabense; blackleg; genetic diversity; potato; soft rot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Diversity of Bacterial Soft Rot-Causing Pectobacterium Species Affecting Cabbage in Serbia.Microorganisms. 2023 Jan 29;11(2):335. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020335. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838301 Free PMC article.
-
Pectobacterium punjabense Causing Blackleg and Soft Rot of Potato: The First Report in the Russian Federation.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 2;13(15):2144. doi: 10.3390/plants13152144. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39124263 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of opportunistic pathogen Pectobacterium polonicum causing potato blackleg in China.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 3;14:1097741. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1097741. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36938006 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diversity of Bacterial Soft Rot-Causing Pectobacterium Species Affecting Cabbage in Serbia.Microorganisms. 2023 Jan 29;11(2):335. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020335. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838301 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogeographic Analysis of Soft-Rot-Causing Pectobacterium spp. Strains Obtained from Cabbage in Serbia.Microorganisms. 2023 Aug 21;11(8):2122. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11082122. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37630682 Free PMC article.
-
Pectobacterium punjabense Causing Blackleg and Soft Rot of Potato: The First Report in the Russian Federation.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 2;13(15):2144. doi: 10.3390/plants13152144. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39124263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Boer S.H. Characterization of pectolytic erwinias as highly sophisticated pathogens of plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2003;109:893–899. doi: 10.1023/B:EJPP.0000003967.34041.65. - DOI
-
- Gijsegem F.V., Toth I.K., Wolf J.M. Soft rot Pectobacteriaceae: A brief overview. In: Gijsegem F.V., Toth I.K., Wolf J.M., editors. Plant Diseases Caused by Dickeya and Pectobacterium Species. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. pp. 1–11. - DOI
-
- Toth I.K., Barny M.A., Brurberg M.B., Condemine G., Czajkowski R., Elphinstone J.G., Helias V., Johnson S.B., Moleleki L.N., Pirhonen M., et al. Pectobacterium and Dickeya: Environment to disease development. In: Gijsegem F.V., Toth I.K., Wolf J.M., editors. Plant Diseases Caused by Dickeya and Pectobacterium Species. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. pp. 39–84. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

