Inhibitory Effect of Thymol on Tympanostomy Tube Biofilms of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 36144469
- PMCID: PMC9505391
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10091867
Inhibitory Effect of Thymol on Tympanostomy Tube Biofilms of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
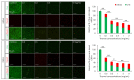
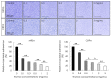
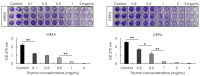
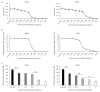
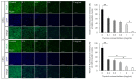
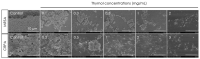
The formation of antibiotic-resistant strain biofilms in tympanostomy tubes results in persistent and refractory otorrhea. In the present study, we investigated the in vitro antibiofilm activity of thymol against biofilms formed by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and ciprofloxacin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (CRPA), using live and dead bacterial staining and adhesion, biofilm formation, biofilm eradication, and biofilm hydrolytic activity assays. The antibiofilm activity of thymol against tympanostomy tube biofilms formed by MRSA and CRPA strains was examined using a scanning electron microscope. In response to thymol treatment, we detected significant concentration-dependent reductions in the viability and adhesion of MRSA and CRPA. Exposure to thymol also inhibited the formation of both MRSA and CRPA biofilms. Furthermore, thymol was observed to enhance the eradication of preformed mature biofilms produced by MRSA and CRPA and also promoted a reduction in the rates of MRSA and CRPA hydrolysis. Exposure to thymol eradicated extracellular polysaccharide present in the biofilm matrix produced by MRSA and CRPA. Additionally, thymol was observed to significantly eradicate MRSA and CRPA biofilms that had formed on the surface on tympanostomy tubes. Collectively, our findings indicate that thymol is an effective inhibitor of MRSA and CRPA biofilms, and accordingly has potential utility as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of biofilm-associated refractory post-tympanostomy tube otorrhea resulting from MRSA and CRPA infection.
Keywords: biofilm; ciprofloxacin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; thymol; tympanostomy tube.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro inhibitory activity of N-acetylcysteine on tympanostomy tube biofilms from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and quinolone-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Nov;126:109622. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109622. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 31404783
-
The use of piperacillin-tazobactam coated tympanostomy tubes against ciprofloxacin-resistant Pseudomonas biofilm formation: an in vitro study.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2009 Feb;73(2):295-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2008.10.020. Epub 2008 Dec 17. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2009. PMID: 19095310
-
Effect of ion-bombarded silicone tympanostomy tube on ciprofloxacin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Oct;76(10):1471-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2012.06.025. Epub 2012 Jul 21. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22819832
-
Effect of vancomycin-coated tympanostomy tubes on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation: in vitro study.J Laryngol Otol. 2010 Jun;124(6):594-8. doi: 10.1017/S0022215109992672. Epub 2010 Jan 8. J Laryngol Otol. 2010. PMID: 20056010 Review.
-
Role of Biofilms in Post-Tympanostomy Tube Otorrhea.Ear Nose Throat J. 2020 Nov;99(1_suppl):22S-29S. doi: 10.1177/0145561320914437. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020. PMID: 32204627 Review.
Cited by
-
Thymol-Loaded Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticles: A Novel Carrier for Enhanced Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity against M. smegmatis through ROS-Mediated Mechanism.Curr Top Med Chem. 2025;25(9):1105-1119. doi: 10.2174/0115680266348684241211072446. Curr Top Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39686638
-
Natural compounds in the fight against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: a review of antibiofilm strategies.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 20;15:1491363. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1491363. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39635434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biofilm-mediated antibiotic tolerance in Staphylococcus aureus from spinal cord stimulation device-related infections.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 29;12(12):e0168324. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01683-24. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39470274 Free PMC article.
-
Thymol-Loaded Eudragit RS30D Cationic Nanoparticles-Based Hydrogels for Topical Application in Wounds: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 21;15(1):19. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010019. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36678648 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of natural compounds on quorum sensing system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a helpful promise for managing biofilm community.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 2;15:1350391. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1350391. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38628638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Dongen T.M., Venekamp R.P., Wensing A.M., Bogaert D., Sanders E.A., Schilder A.G. Acute otorrhea in children with tympanostomy tubes: Prevalence of bacteria and viruses in the post-pneumococcal conjugate vaccine era. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015;34:355–360. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000000595. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

