Extraction, Physicochemical Properties, Anti-Aging, and Antioxidant Activities of Polysaccharides from Industrial Hemp Residues
- PMID: 36144481
- PMCID: PMC9503781
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27185746
Extraction, Physicochemical Properties, Anti-Aging, and Antioxidant Activities of Polysaccharides from Industrial Hemp Residues
Abstract
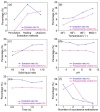
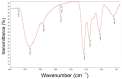
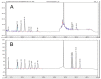
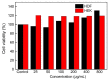
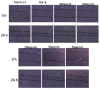
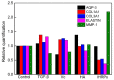
A large amount of hemp polysaccharides remain in industrial hemp residues (IHR) after cannabidiol extraction, resulting in the waste of resources. Therefore, the systematic study of hemp polysaccharides is beneficial to the development of IHR in the future. In this study, the extraction of industrial hemp residues polysaccharide (IHRPs) was optimized by single-factor experiment and orthogonal experimental design. The optimum heating extraction conditions were extraction temperature 98 °C, solid-liquid ratio 1:10, extraction time 1 h, number of successive extractions 2, and pH at 4. The extraction ratio and the polysaccharide content were 20.12 ± 0.55% and 12.35 ± 0.26% at the conditions, respectively. Besides, the best alcohol precipitation conditions were pumping with 2 L/h, stirring continuously, and ice-water bath for 4 h. The crude IHRPs was further purified by column chromatography and the polysaccharide/protein contents of purified IHRPs were 34.44% and 1.61%. IHRPs was mainly made up of ten monosaccharides and some non-sugar components including organic acids, flavonoids, steroids, and glycoside. The FT-IR demonstrated the polysaccharide skeleton of IHRPs. Moreover, the DPPH and ABTS scavenging rate of IHRPs were 76.00% and 99.05% at the concentrations of 1 mg/mL. IHRPs could promote the epidermal cells proliferation and healing of cell scratches. Meanwhile, IHRPs could promoted the expression of anti-aging-related genes. Overall, IHRPs could be a desirable natural source of antioxidants and anti-aging products in many aspects.
Keywords: anti-aging activity; antioxidant activity; extraction; industrial hemp; polysaccharide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extraction, purification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from cold pressed oil cake of 'Tengjiao' seed.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Nov 15;163:508-518. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.207. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32615223
-
Optimization of the Extraction Process and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharide Extracted from Centipeda minima.Chem Biodivers. 2023 Jan;20(1):e202200626. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202200626. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Chem Biodivers. 2023. PMID: 36448941
-
Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of Platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharides and evaluation of its structural, antioxidant and hypoglycemic activity.Ultrason Sonochem. 2023 Nov;100:106635. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106635. Epub 2023 Oct 7. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023. PMID: 37839233 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabidiol (CBD) as an emerging nutraceutical ingredient from industrial hemp: regulation, production, extraction, nutraceutical properties, and functionality.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Dec 9:1-23. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2436130. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39654401 Review.
-
An important polysaccharide from fermentum.Food Chem X. 2022 Jul 8;15:100388. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100388. eCollection 2022 Oct 30. Food Chem X. 2022. PMID: 36211774 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical and Functional Diversity of Enzyme-Assisted Extracts from Hippophae rhamnoides L., Aralia cordata Thunb., and Cannabis sativa L.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 5;13(8):950. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080950. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199196 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharides with Arabinose: Key Players in Reducing Chronic Inflammation and Enhancing Immune Health in Aging.Molecules. 2025 Mar 6;30(5):1178. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051178. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of Polysaccharides from Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Kernels.Foods. 2024 Oct 28;13(21):3429. doi: 10.3390/foods13213429. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39517213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shoyama Y., Yagi M., Nishioka I., Yamauchi T. Biosynthesis of cannabinoid acids. Phytochemistry. 1975;14:2189–2192. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(00)91096-3. - DOI
-
- De Meijer E.D., Van der Kamp H., Van Eeuwijk F. Characterisation of Cannabis accessions with regard to cannabinoid content in relation to other plant characters. Euphytica. 1992;62:187–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00041753. - DOI
-
- Luca S.V., Roehrer S., Kleigrewe K., Minceva M. Approach for simultaneous cannabidiol isolation and pesticide removal from hemp extracts with liquid-liquid chromatography. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020;155:112726. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112726. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

